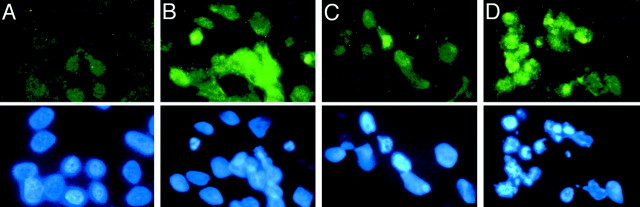
Fig. 4.
Chronic rotenone treatment caused oxidative DNA damage. Control cells (A, C) and cells treated with rotenone for 4 weeks (B, D) were stained with antibodies against 8-oxo-dG, a marker of oxidative DNA damage (top panels). The same cells were also labeled with bisbenzimide for nuclear morphology (bottom panels). Rotenone-treated cells showed increased 8-oxo-dG immunoreactivity before H2O2 exposure (B). H2O2 increased 8-oxo-dG staining to a greater extent in rotenone-treated cells (D) than in control cells (C). Many cells with oxidative DNA damage showed fragmented nuclear morphology characteristic of apoptosis (B, D). Similar results were observed in four replicates.