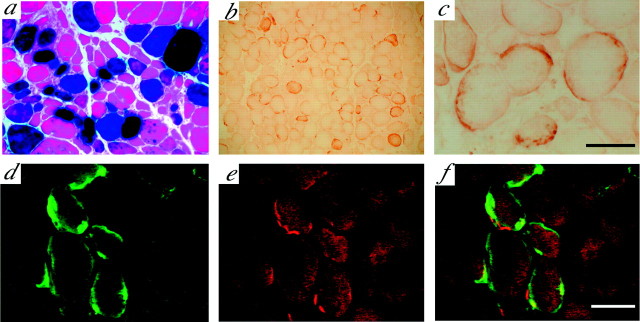
Fig. 1.
Characterization and muscle expression of AAV vector-transduced genes after injection into gastrocnemius muscles. 5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-d-galactopyranoside-stained cross sections from control ALS mice after an injection with AAV-LacZ vector at 110 d of age (a). FLAG immunoreactivity is observed around the injection sites in AAV-GDNF vector-treated ALS mice of the same age (b; low magnification). At higher magnification (c), intense immunoreactivity can be seen to be mainly localized in the vicinity of the sarcolemma as well as surrounding regions, suggesting secreted expression of transgene-derived GDNF after intramuscular AAV-GDNF vector injection. More intense immunoreactivity for FLAG (d) was localized to postsynaptic AChR-rich regions, as confirmed by double staining with rhodamine-labeled α-bungarotoxin (e), indicating the accumulation of transgene-derived GDNF at neuromuscular junctions. f, Merging of c and d. Scale bars: (inc) a, 100 μm; b, 200 μm; c, 50 μm; (in f)d–f, 50 μm.