Fig. 6.
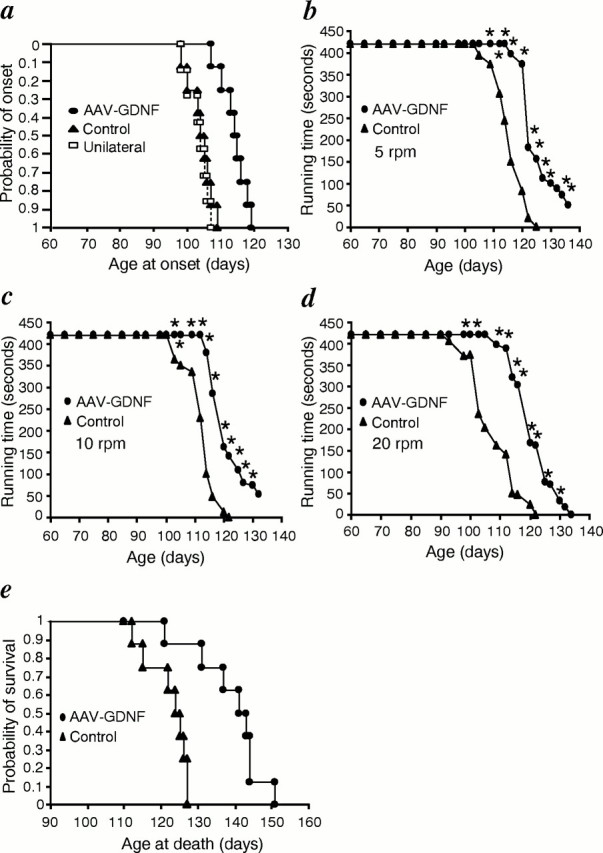
a, General behavior test for ALS mice. Cumulative probability of onset of rotarod deficits in ALS mice. The AAV-GDNF vector-treated mice had an age of onset of 114.0 ± 4.0 d (n = 12) compared with 101.3 ± 5.4 d (n = 11) for control ALS mice and 102.7 ± 3.1 d (n = 7) for unilaterally AAV-GDNF vector-treated mice. AAV-GDNF vector treatment significantly delayed disease onset by ∼13 d compared with in control ALS mice (p < 0.01), whereas the onset in unilateral AAV-GDNF vector-treated mice did not show a significant difference from that in control ALS mice. Performance of ALS mice in the rotarod test at 5 rpm (b), 10 rpm (c), and 20 rpm (d). AAV-GDNF vector-treated ALS mice performed significantly better than control ALS mice (n = 8; *p < 0.05).e, Cumulative probability of survival. Survival was significantly prolonged by ∼17 d in AAV-GDNF vector-treated ALS mice when compared with in control transgenic ALS littermates treated with the vehicle or AAV-LacZ vector (n = 8;p < 0.01).
