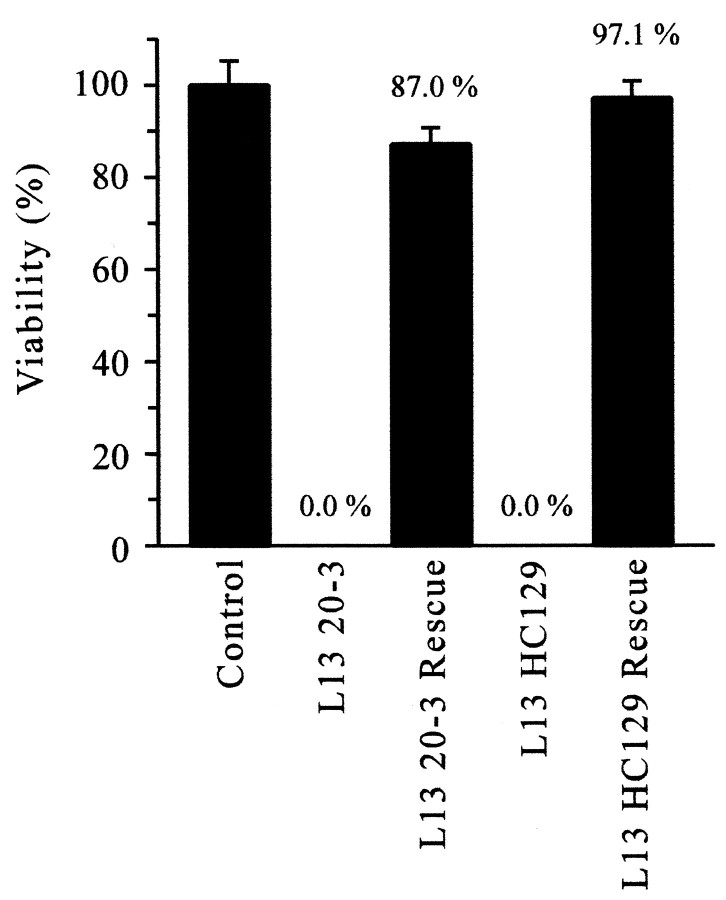
Fig. 6.
Rescue of cac lethal mutants. Three different crosses were performed to determine the adult viability of each cac lethal mutant and rescued caclethal mutant relative to males carrying a WT X chromosome (percentage viability; see Materials and Methods). +;;UAS-cac1/+ males (Control) served as a reference for WT viability. In the absence of aUAS-cac1 transgene, elav-GAL4 l(1)L1320-3 (L13 20-3) andelav-GAL4 l(1)L13HC129 (L13 HC129) males were never observed, indicating uniform lethality. In contrast, males of the genotypes elav-GAL4 l(1)L1320-3;;UAS-cac1/+ (L13 20-3 Rescue) and elav-GAL4 l(1)L13HC129;;UAS-cac1/+ (L13 HC129 Rescue) were clearly rescued and exhibited viability similar to that of WT controls. The mean percentage viability value obtained from five independent rescue experiments for each genotype (n = 5) is indicated. Viability ofL13 20-3 Rescue and L13 HC129 Rescue males was not significantly different from that of control males (p > 0.05).