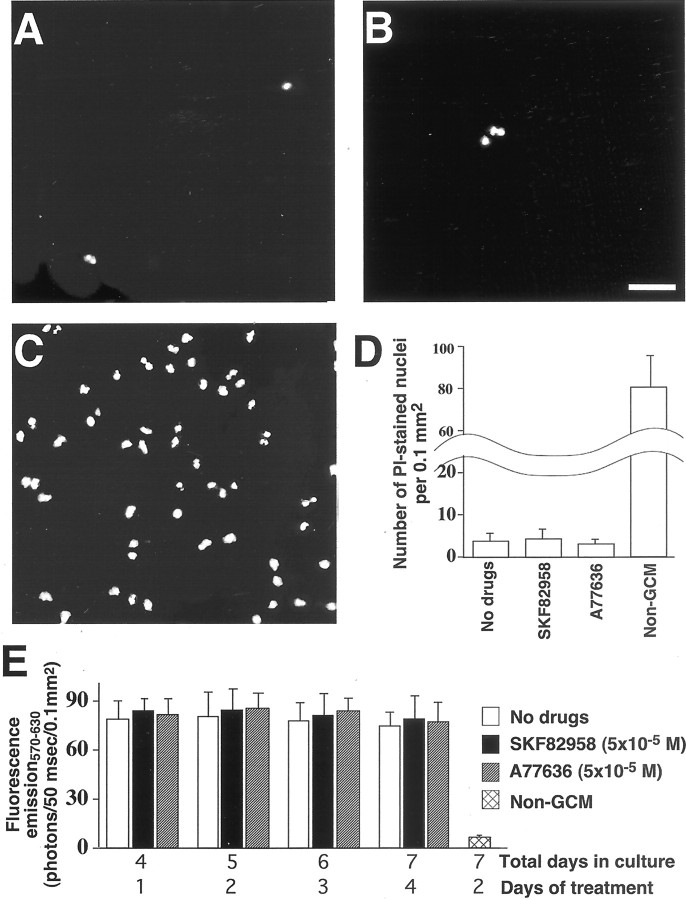
Fig. 2.
Analysis of cell viability in cortical cultures.A–C, PI staining of apoptotic–necrotic nuclei in live cultures of cortical cells obtained from the frontal lobe of E15 mouse fetuses and cultured for 7 d. A, Cultures grown in the absence of D1R antagonists; B, cultures that for the last 96 hr of culturing were exposed to 5 × 10−5m of the D1R agonist, SKF82958.C, Cultures in which cell death was induced by 48 hr exposure to glia-unconditioned medium (Non-GCM). Scale bar, 25 μm. D, Histogram showing the density of PI-stained apoptotic–necrotic nuclei in cultures of cortical cells obtained from the frontal lobe of E15 mouse fetuses, which after 3 d of drug-free culturing were grown for 96 hr either in the absence of D1R-specific ligands or in the presence of 5 × 10−5m of the D1R agonists, SKF82958 and A77636. E, Histogram showing fluorescence resulting from MTT transformation in mitochondria of live cells in cultures of cortical cells obtained from the frontal lobe of E15 mouse fetuses, which after 3 d of drug-free culturing were grown for an additional 24–96 hr either in the absence of D1R-specific ligands or in the presence of 5 × 10−5m of SKF82958 or A77636. Histograms D and Ealso include control cultures in which cell death was induced by 48 hr exposure to non-GCM. In both histograms, each columnrepresents the mean value from seven separately generated cultures ± SEM. Note that D1R agonist exposure does not induce a significant decrease in the viability of cultured cortical cells.