Fig. 6.
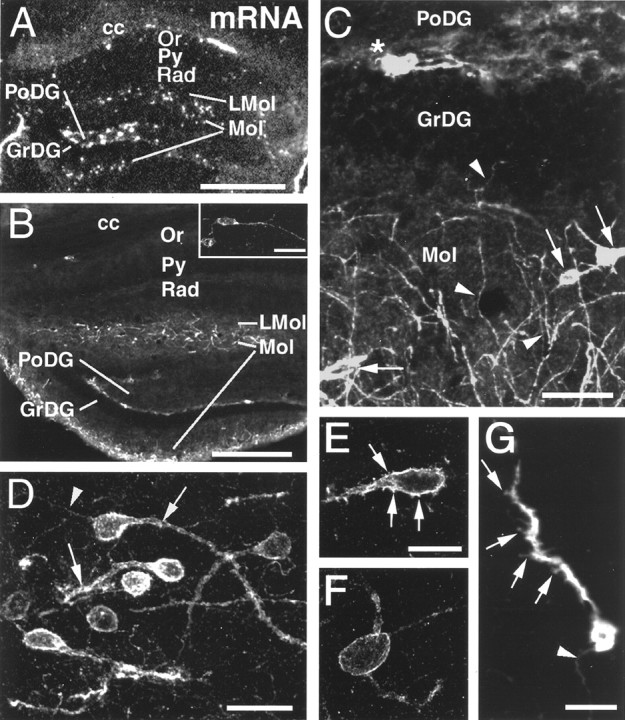
CXCR4 mRNA expression and cellular localization of CXCR4-LIR in the hippocampal formation. Coronal sections are shown in a dark-field micrograph after in situ hybridization (A) and in confocal images after fluorescent immunohistochemistry (B–G). A, B, Low-power micrographs comparing the distribution of CXCR4 mRNA (A) and CXCR4-LIR (B); note corpus callosum (cc) for orientation. In the oriens layer (Or), few CXCR4 mRNA-expressing and CXCR4-LIR neurons are detectable (shown at higher magnification in B), but none are detectable in the pyramidal cell layer (Py), stratum radiatum (Rad), or granular layer (GrDG). In the lacunosum moleculare layer (LMol), in the molecular layer (Mol), and at the border of the granular and polymorphic layers (PoDG), numerous CXCR4 mRNA-expressing and CXCR4-ir neurons are detected. Within the polymorphic layer, neurons express high CXCR4 mRNA levels but exhibit no detectable somatodendritic CXCR4-LIR.C–G, High-power confocal images demonstrating the subcellular targeting of CXCR4-LIR. C, In neurons of the molecular layer, CXCR4-LIR is somatodendritic (C,arrows) and axonal (C,arrowheads). Note the perpendicular orientation of several CXCR4-ir axons to the granular layer (C,arrowheads in GrDG andMol). At the border of the granular and polymorphic layers, CXCR4-LIR is restricted to neuronal perikarya and their proximal dendrites (C, asterisk).D, In the lacunosum moleculare layer, CXCR4-LIR typically exhibits somatodendritic (D,arrows) and axonal targeting (D,arrowhead) in parallel orientation to the hippocampal fissure. E–G, CXCR4-ir neurons in the molecular and lacunosum moleculare layers either exhibit CXCR4-ir spine-like protrusions at their cell bodies and dendrites (E,G, arrows) or exhibit a spine-free morphology (F). G, Note the CXCR4-ir axon (arrowhead). Scale bars: A, 400 μm; B, 300 μm; inset inB, 30 μm; C, 40 μm; D, 20 μm; E, F, 10 μm; G, 15 μm.
