Fig. 3.
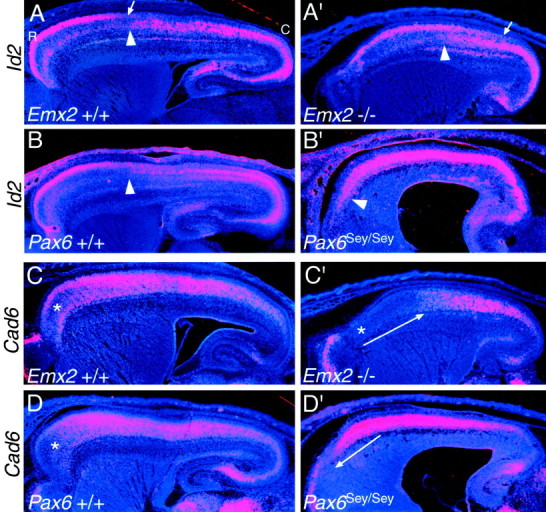
Id2 and Cad6, used as markers of rostral neocortical areas, show opposing shifts inEmx2 and Pax6 mutants. In situ hybridizations on sagittal sections through the forebrain of E18.5 mice using S35-labeled riboprobes for the HLH transcription factor, Id2(A–B′) or the cadherin,Cad6 (C–D′), and counterstained with bisbenzimide are shown. Sections are fromEmx2 wild-type (+/+) and mutant (−/−) littermates orPax6 wild-type (+/+) and mutant (Sey/Sey) littermates and are taken from similar medial–lateral positions. Eachpanel is a montage of single-exposure photos using dark-field illumination with a red filter to view the silver grains and UV fluorescence to view the counterstain. Id2 exhibits a graded expression in superficial layers of rostral areas in wild-type mice; the arrows in A and A′ mark the position where the expression declines to very low levels. Thearrowheads in A–B′ mark the transition from low to high expression reported in layer 5; this transition corresponds to the border between motor and somatosensory areas. The asterisks in C, C′, andD mark a domain of low Cad6 expression normally characteristic of far rostral neocortex. This domain of low expression expands and shifts caudally in Emx2 mutants, whereas inPax6 mutants it shifts rostrally and essentially disappears (C′, D′, long arrows). See Results for details. C, Caudal; R, rostral.
