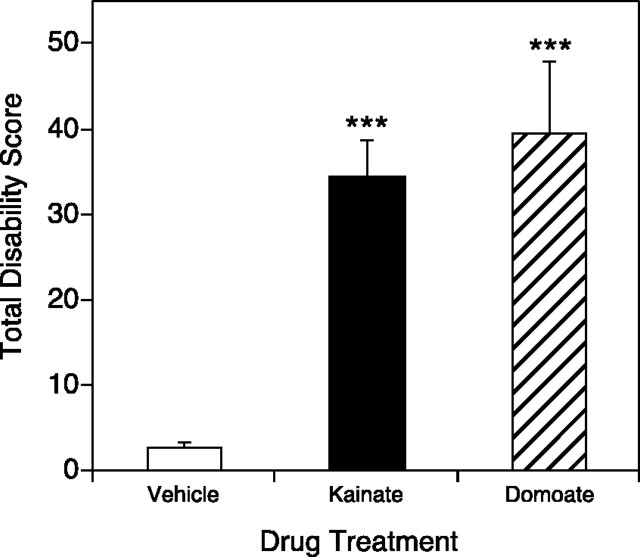
Fig. 9.
Domoic acid microinjection into the cerebellum induced dystonia in normal mice. Domoate was injected into the medial cerebellum, and disability scores were recorded every 10 min for 2 hr; total disability score represents the sum of the scores for the entire 2 hr observation period. Data represent means ± SEM (n = 5 per group). ***p < 0.001, indicates a significant increase in dystonia over vehicle microinjection in domoate- and kainate-treated mice (one-factor ANOVA; Scheffe's post hoc analysis). Domoate-induced dystonia was not significantly different from kainate-induced dystonia.