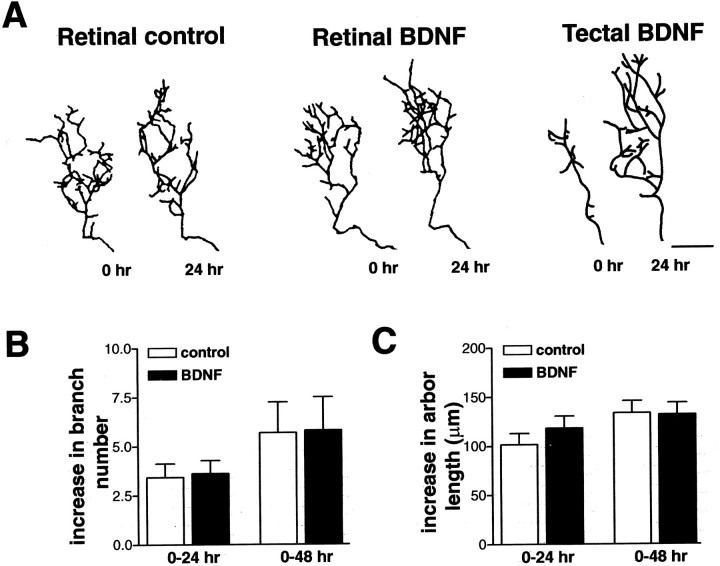
Fig. 6.
RGC axon arbor complexity is unaffected by retinal BDNF levels. To determine whether retinal BDNF influences RGC axon arborization at a distance, tadpoles were intraocularly injected with control, BDNF-, or anti-BDNF-treated microspheres, and the resulting changes in RGC axon arbor dynamics were compared with tectally applied BDNF (Cohen-Cory and Fraser, 1995; Lom and Cohen-Cory, 1999). A, Individual RGC axon arbor morphologies of control, retinal BDNF, and tectal BDNF at 0 and 24 hr after treatment demonstrate that only tectally applied BDNF significantly alters RGC axon arborization. B, C, Altering retinal BDNF levels had no significant effects on RGC axon arbor complexity as measured by the increase in total branch number (B) and total arbor length (C) 24 and 48 hr after treatment (p > 0.05). Error bars indicate SEM. Scale bar, 20 μm.