Fig. 6.
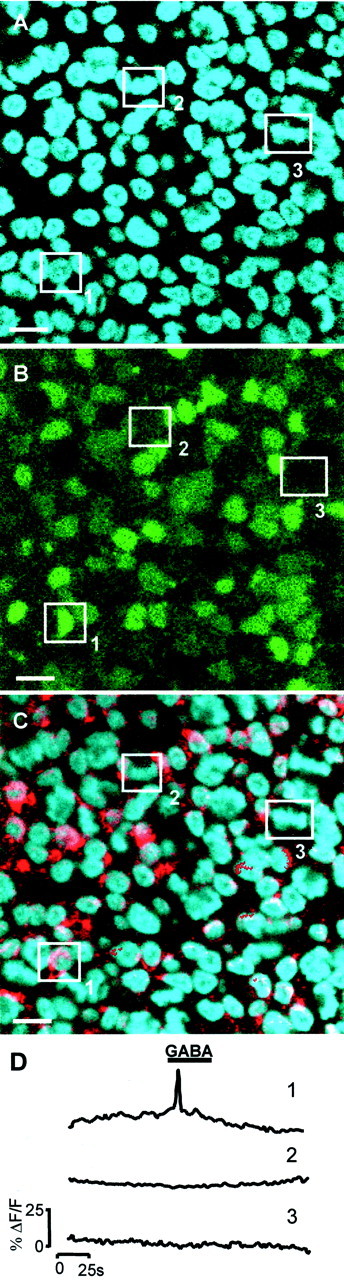
The responses to GABA arise primarily from newly differentiated neurons. A–C, Single confocal sections through the VZ of the same region within an E6 chick retina.A, Hoechst 33342 staining to show the mitotic status of cells (cell indicated by box 1 is in interphase; those in boxes 2 and3 are mitotic). B, Fluo-4 image taken during the application of GABA (100 μm).C, Identification of differentiating neurons using TuJ-1 conjugated with Cy5 (red) and Hoechst 33342 (blue). The same three cells are highlighted throughout. Scale bar, 5 μm. D, Change in [Ca2+]i (ΔF/F) in cells1–3 in response to GABA.Cell1 is in interphase, is TuJ-1 positive, and responds to GABA; cell 2 is in interphase, is TuJ-1 negative, and does not respond to GABA; and cell 3 is mitotic, is TuJ-1 negative, and does not respond to GABA.
