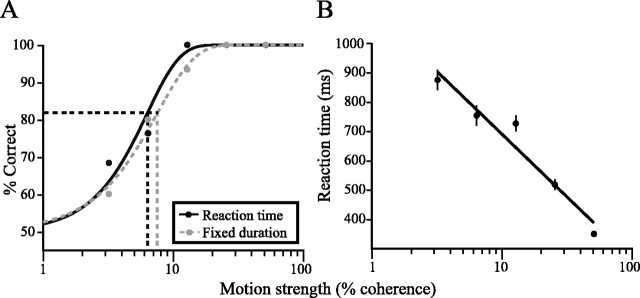
Fig. 3.
Behavioral data from one experiment. A, Psychometric functions from RT and FD versions of the direction discrimination task. RT and FD tasks were performed in alternating blocks of ∼60 trials. The probability of a correct direction judgment is plotted as a function of motion strength and fit by sigmoid functions (see Materials and Methods, Eq. 1). Vertical linesindicate psychophysical thresholds (α in Eq. 1): the motion strength that would support 82% correct choices (horizontal dashed line). B, Effect of motion strength on reaction time. Mean RT (± SEM) was obtained from correct trials in the experiment inA (RT block). The line is a least squares regression of RT versus log motion coherence (p< 0.001).