Fig. 1.
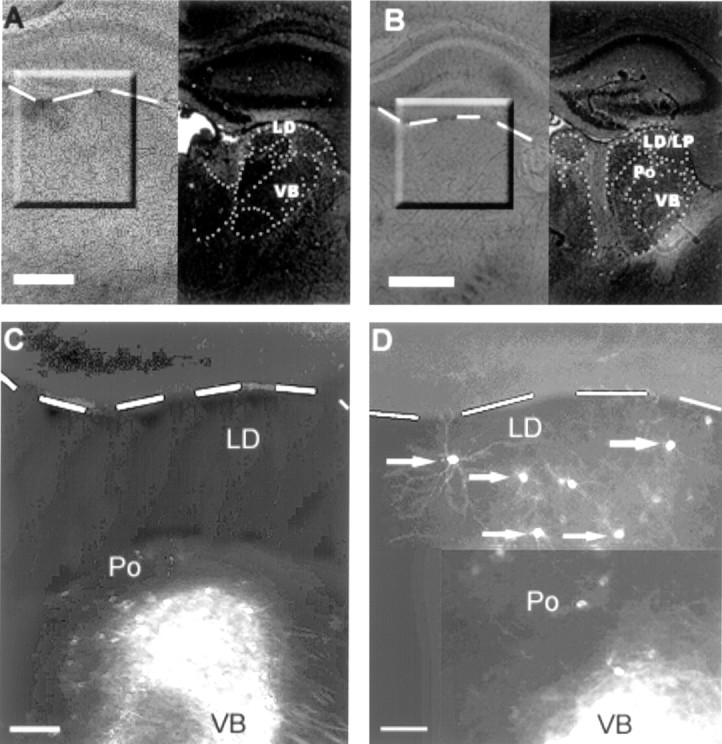
Low-power photomicrographs of coronal brain sections from wild-type (A, C) and ephrin-A5 knock-out (B, D) animals after implantation of DiI in the sensorimotor cortical region of P8 mice.A and B show bright-field photographs of the slices labeled with DiI (left) and cresyl violet staining for identification of the thalamic nuclei (right). C and Dcorrespond to the marked areas in A andB, and the dashed line indicates the border between hippocampus and dorsal thalamus. Note that, inC, cells are concentrated in ventral portions of the thalamus, a region corresponding to Po and VB. In D, after placement of DiI in a cortical region similar toC, cells are stained not only in the Po/VB region but also dorsally in LD; some of these cells are indicated by anarrow. Scale bars: A,B, 200 μm; C, D, 100 μm.
