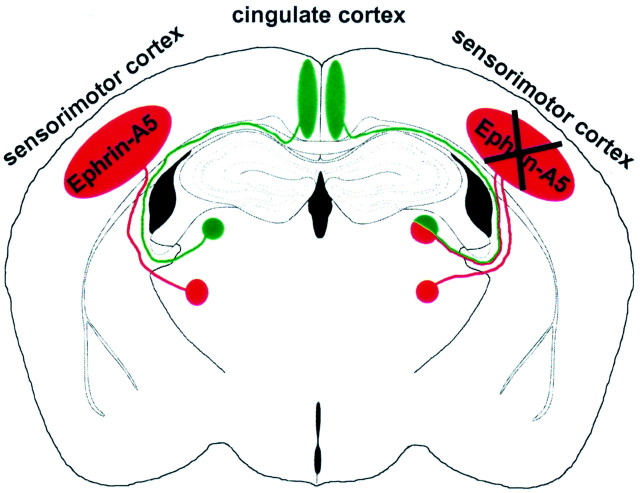
Fig. 5.
Schematic representation of thalamocortical projections in wild-type (left) and ephrin-A5 −/− (right) mice. Thalamic neurons in ventrobasal nuclei (red circle) project to the sensorimotor cortex (red ellipse), and limbic thalamic neurons in laterodorsal nuclei (green circle) project to the cingulate cortex (green ellipse). However, in knock-out animals, limbic thalamic neurons also formed additional projections to the sensorimotor cortex (indicated by red–green lines on the right). The portion of miswired cells was variable (see Table 1) and is overrepresented in this schematic figure. These data suggest that ephrin-A5 acts as a repulsive guidance cue that restricts limbic thalamic axons from innervating inappropriate cortical regions.