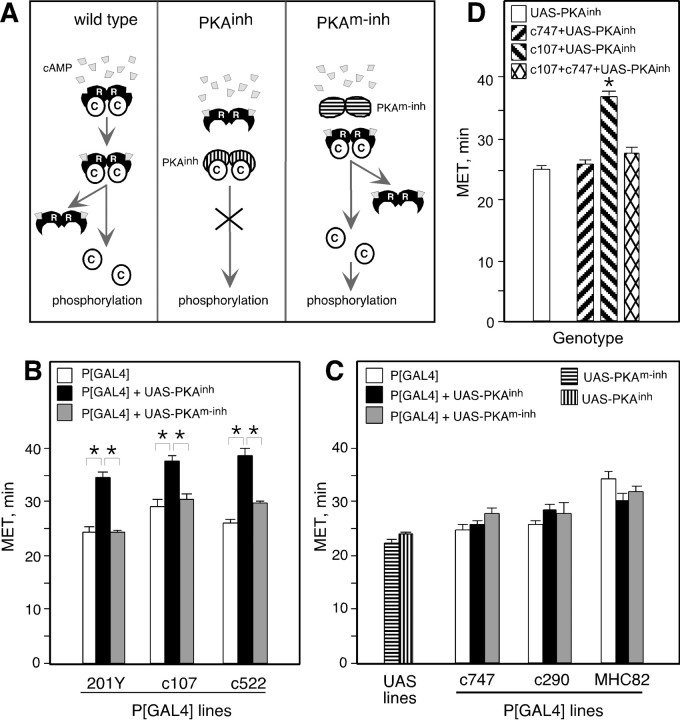
Fig. 1.
Expression of PKAinh in specific brain regions alters ethanol sensitivity in the inebriometer. A, Inactive PKA holoenzymes consist of two regulatory (R) and two catalytic (C) subunits. Binding of cAMP to R subunits results in their dissociation from C and hence C activation. PKAinh lacks cAMP binding ability and remains bound to C even on increases in cellular cAMP, thereby inhibiting C activation. PKAm-inh is unable to bind cAMP or C and therefore should not have an inhibitory effect. B, PKAinh expression under the control of 201Y, c107, and c522 resulted in increased MET. One-way ANOVA revealed a significant effect of genotype for all three P[GAL4] lines: 201Y (F(2,24) = 24.2; p< 0.0001), c107 (F(2,15) = 14.8;p < 0.0001), and c522 (F(2,15) = 28.1; p< 0.0001). Pair-wise planned comparisons, with the criticalp value adjusted to α = 0.0167, revealed significant differences between P[GAL4]+UAS-PKAinhand both P[GAL4] and P[GAL4]+UAS-PKAm-inh(p < 0.001 for all comparisons). Pairwise planned comparisons did not reveal significant differences between P[GAL4] and P[GAL4]+UAS-PKAm-inh: 201Y (p = 0.966), c107 (p = 0.346), and c522 (p = 0.061). For each P[GAL4] line,n is the same for P[GAL4], P[GAL4]+UAS-PKAinh, and P[GAL4]+UAS-PKAm-inh: 201Y (n= 9), c107 (n = 6), c522 (n = 6), c747 (n = 8), c290 (n = 5), MHC82 (n = 7), UAS-PKAinh(n = 59), and UAS-PKAm-inh(n = 20). Asterisks denote significant differences. In all figures, error bars indicate SEM. In this and subsequent figures, flies were heterozygous for autosomal insertions and hemizygous for X-linked insertions (see Materials and Methods for chromosomal location of insertions).C, The MET of c747, c290, and MHC82 P[GAL4] lines was not altered by the presence of UAS-PKAinh or UAS-PKAm-inh. One-way ANOVA comparing P[GAL4], P[GAL4]+UAS-PKAinh, and P[GAL4]+UAS-PKAm-inh revealed no significant effect of genotype for c290 (F(2,12) = 1.35; p = 0.30) and MHC82 (F(2,18) = 2.93; p= 0.078). For c747, there was a weak effect of genotype (F(2,21) = 4.0; p = 0.038). Planned pair-wise comparisons, with the criticalp value adjusted to α = 0.0167, revealed a marginally significant difference between c747+UAS-PKAm-inh and c747 (p = 0.012) but not between c747+UAS-PKAm-inh and c747+UAS-PKAinh (p = 0.061) or between c747+UAS-PKAinh and c747 (p = 0.459). D, Expression of PKAinh under the control of c107 and c747 resulted in normal MET. t tests with the criticalp value adjusted to α = 0.025 revealed no significant difference between c107+c747+UAS-PKAinhand c747+UAS-PKAinh (p = 0.05) but did reveal a significant difference between c107+c747+UAS-PKAinh and c107+UAS-PKAinh (p < 0.0001). The UAS-PKAinh MET is fromB. n = 10 for c747+UAS-PKAinh and c107+UAS-PKAinh; n = 8 for c107+c747+UAS-PKAinh.