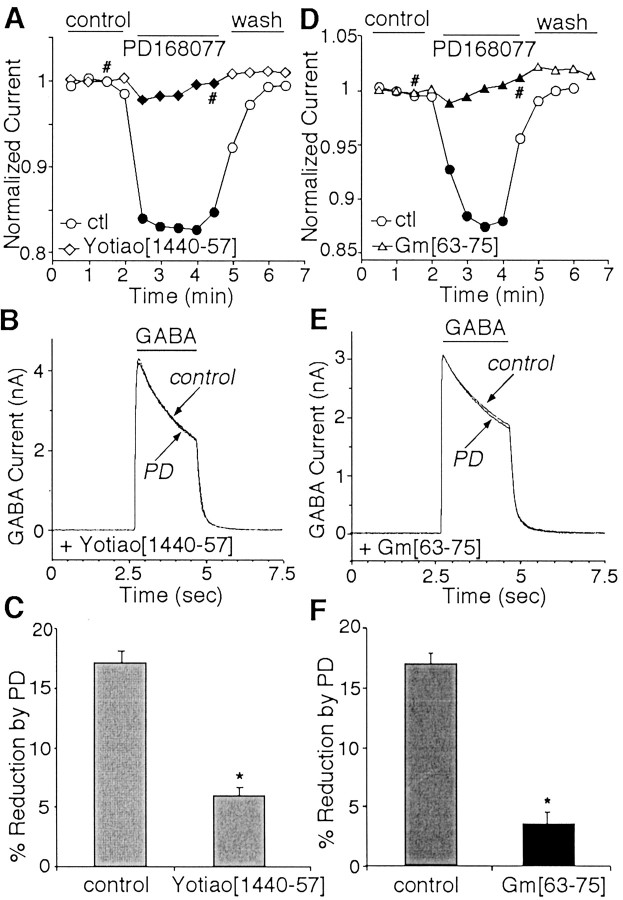
Fig. 7.
The D4 modulation of GABAAreceptor currents required anchoring of the PKA/PP1 complex to the channel by Yotiao. A, Plot of peak GABAAcurrent as a function of time and agonist application with the PKA anchoring inhibitory peptide Yotiao[1440–1457] (10 μm,diamonds) or the control (ctl) peptide sYotiao[1440–1457] (10 μm,circles) in the recording pipette. B, Representative current traces taken from the records used to construct A (at time points denoted by #).C, Cumulative data (means ± SEM) showing the percentage modulation of GABAA currents by PD168077 (PD; 20 μm) in the presence of Yotiao[1440–1457] peptide (n = 12) or the scrambled control peptide sYotiao[1440–1457] (n= 7). *p < 0.005; ANOVA. D, Plot of peak GABAA current as a function of time and agonist application with the PP1 anchoring inhibitory peptide Gm[63–75] (10 μm, triangles) or the control peptide sGm[63–75] (10 μm, circles) in the recording pipette. E, Representative currenttraces taken from the records used to constructD (at time points denoted by #). F, Cumulative data (means ± SEM) showing the percentage modulation of GABAA currents by PD168077 (20 μm) in the presence of Gm[63–75] peptide (n = 14) or the scrambled control peptide sGm[63–75] (n = 8). *p < 0.005; ANOVA.