Fig. 5.
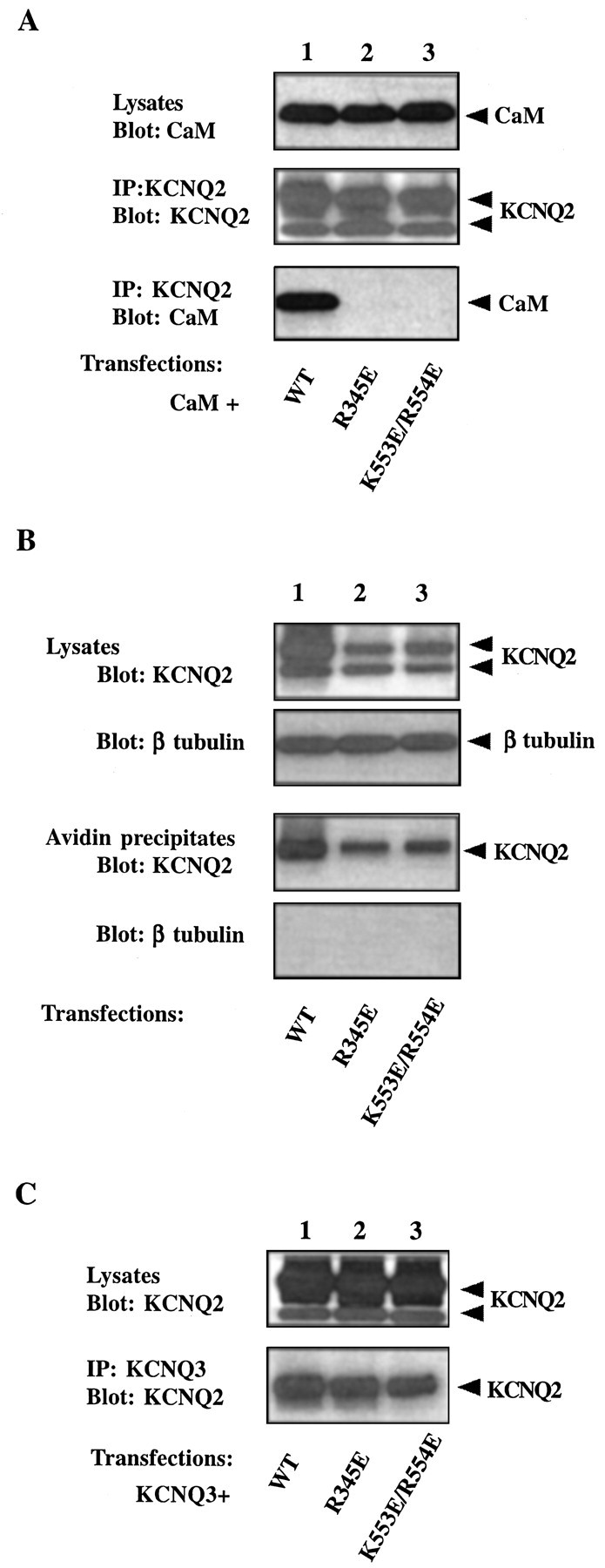
Properties of two KCNQ2 channels with mutations in CaM-binding sites. A, R345E and K553E/R554E KCNQ2 do not coimmunoprecipitate with CaM. HA-tagged CaM was coexpressed with one of the following V5-tagged KCNQ2 constructs in tsA 201 cells: wild type (lane 1), R345E (lane 2), or K553E/R554E (lane 3). Cell lysates were probed for the expression of CaM with anti-HA (top panel). KCNQ2 channel immunoprecipitates were probed for the channel with anti-V5 (middle panel) and for CaM with anti-HA (bottom panel). CaM is detected in immunoprecipitates of wild-type, but not mutant, channels. B, R345E and K553E/R554E KCNQ2 are expressed on the cell surface. tsA 201 cells were transfected with V5-tagged KCNQ2 channels. Cell surface proteins were biotinylated by a membrane-impermeable reagent and isolated by streptavidin beads. Channel immunoreactivity in the lysates (first panel) and in the streptavidin precipitates (third panel) was detected with the anti-V5 antibody. The proportions of mutant channels (lanes 2, 3) targeted to the surface are comparable with those of the wild-type KCNQ2 (lane 1). The biotinylation reagent did not label an intracellular protein, β-tubulin (secondand fourth panels), confirming its specificity for cell surface proteins. C, R345E and K553E/R554E KCNQ2 still coimmunoprecipitate with KCNQ3. C-Myc-tagged KCNQ3 channel was transfected together with one of the V5-tagged KCNQ2 channels into tsA 201 cells. The KCNQ3 channel was pulled down with anti-Myc antibody, and the lysates (top panel) and immunoprecipitates (bottom panel) were probed for KCNQ2 with anti-V5. Both wild-type (lane 1) and mutant KCNQ2 channels (lanes 2, 3) immunoprecipitate with KCNQ3. Note that in B and C thetop band of the KCNQ2 doublet in the cell lysates is enriched in the streptavidin or anti-KCNQ3 precipitates.
