Fig. 4.
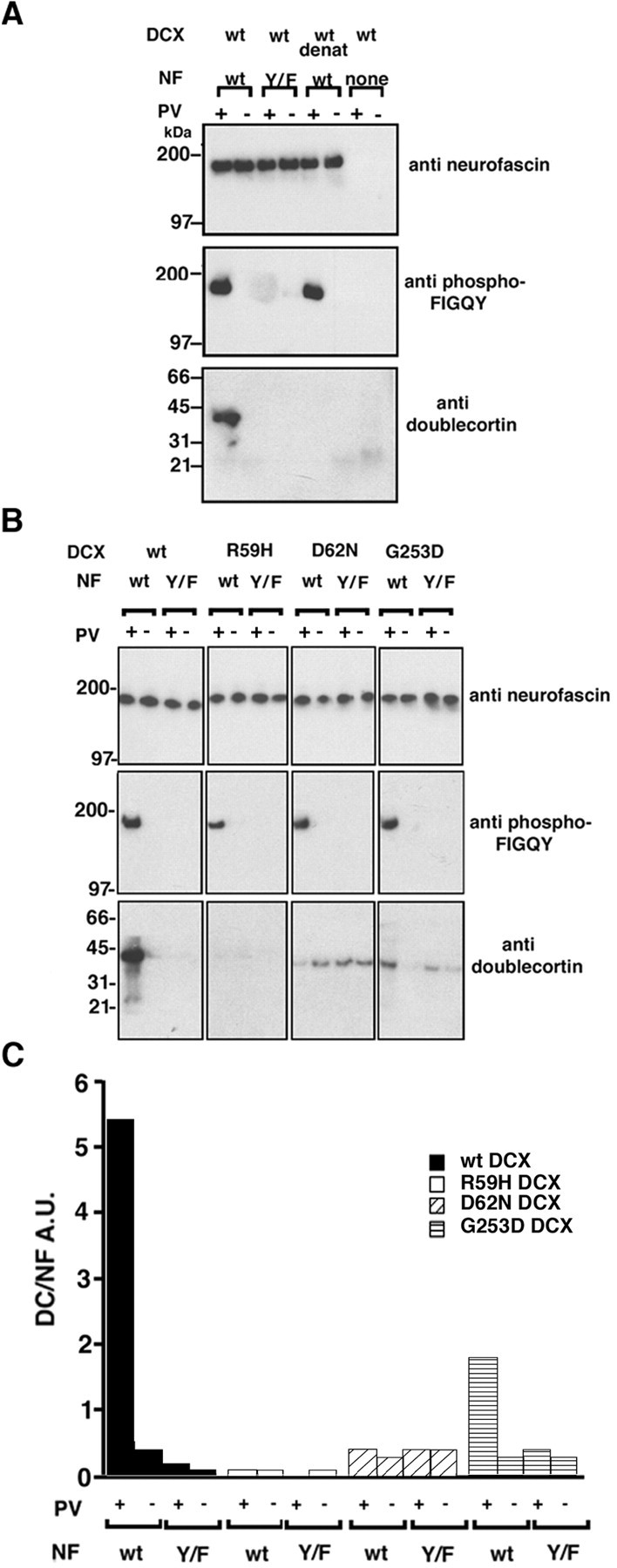
Doublecortin binds directly to FIGQY tyrosine-phoshorylated full-length neurofascin. A, Phospho-FIGQY native neurofascin binds doublecortin in the in vitro binding assay (Materials and Methods). B, Mutants of doublecortin that cause neuronal migration defects do not bind to full-length neurofascin. In A andB, the antibodies used for immunoblotting are shown to the right of the blots. The doublecortin proteins used are shown above each of thefour columns of blots. InA and B, pervanadate treatment of the B104 cells transfected with HA-tagged neurofascin before immunoprecipitation is indicated by +, and the lack of treatment is indicated by − above the blots. The type of neurofascin is indicated above the blots inA and B: wt, wild type;Y/F, FIGQY/F neurofascin. In A,none indicates nonspecific mouse IgG used instead of anti-HA antibody. In A, wild-type purified doublecortin was used in all binding sets as indicated above theblots; wt denat refers to heat-denatured wild-type doublecortin. In B the identities of doublecortin proteins used are shown above each of the four columns of blots. C, Graphical representation of the results of the binding assay shown inB. The y-axis represents in arbitrary units the ratio of doublecortin signal to the neurofascin signal after background correction. The neurofascin used in the binding is shown below the x-axis. wt, Wild type;Y/F, FIGQY/F neurofascin. Pervanadate treatment or lack of it is indicated by + or −, respectively. Black barsrepresent binding for wild-type doublecortin, white barsrepresent binding for R59H doublecortin, diagonally striped bars represent binding for D62N doublecortin, andhorizontally striped bars represent binding for G253D doublecortin. DCX, Doublecortin; NF, neurofascin; PV, pervanadate.
