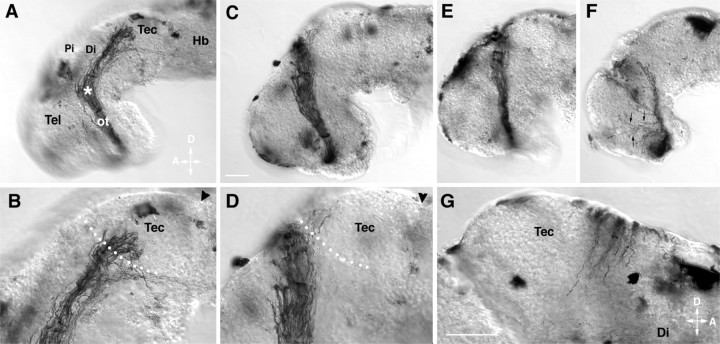
Fig. 1.
RGC axons make improper guidance decisions in the presence of the metalloprotease inhibitor GM6001.A–G, Representative examples of stage 40 whole-mount brain preparations showing the HRP-labeled optic projection in a control brain (A, B) and when GM6001 was applied to the exposed brain (C–G). B andD are higher-power views of A andC, respectively. C, D, A 1 μm concentration of GM6001. E, A 10 μm concentration of GM6001. F, A 20 μm concentration of GM6001. G, Axons cross over the dorsal midline into the contralateral brain of a 1 μm GM6001-treated brain. Tec, Tectum;Pi, pineal gland; Di, diencephalon;Tel, telencephalon; ot, optic tract;Hb, hindbrain; D, dorsal;A, anterior. Arrowheads mark the midbrain–hindbrain isthmus; the asterisk marks the caudal turn of the optic projection in the mid-diencephalon, andarrows in F show axons growing aberrantly in the telencephalon. White dots show the approximate anterior border of the optic tectum. Scale bars: C, 50 μm; A, C, 65 μm for E andF; and G, 50 μm for B,D, and G.