Fig. 3.
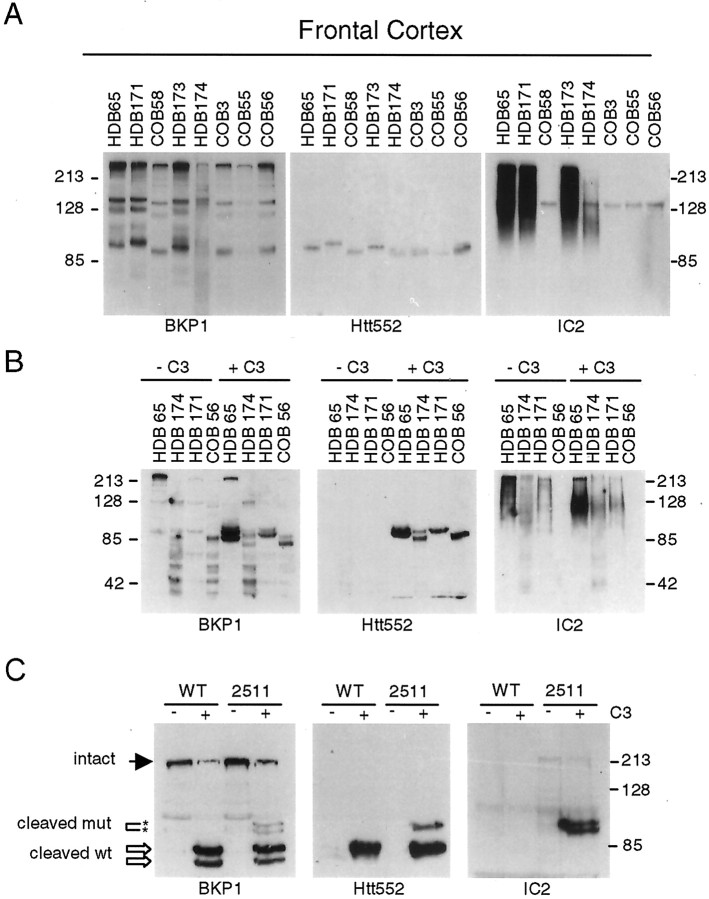
Htt is cleaved at amino acid 552 in vivo. A, Parallel blots prepared from human cortex homogenized in the presence of zVAD-fmk were probed with BKP1, Htt552, and 1C2. Cleavage products showing CAG-dependent mobility are detected by BKP1 (left panel) in all samples except HD brain (HDB) 174 (in this exposure) and by Htt552 (center panel) but not 1C2 (right panel). B, Human postmortem tissue was homogenized in the absence of zVAD-fmk and incubated at 37°C with or without 2 μm recombinant caspase-3. Replicate blots were probed with BKP1 (left panel), Htt552 (center panel), or 1C2 (right panel). Caspase cleavage products arising from wild-type or expanded human htt in human brain lysates are detected with BKP1 and Htt552 but not 1C2. COB, Control brain.C, Whole murine brain from 6-month-old wild-type (WT) or YAC72 (line 2511) transgenic mice was homogenized in the absence of zVAD-fmk and incubated at 37°C with (+) or without (−) caspase-3 (C3). Replicate blots were probed with BKP1 (left panel), Htt552 (center panel), or 1C2 (right panel). Caspase cleavage products arising from wild-type murine (double open arrow) or expanded human htt (double asterisk) are distinguishable by the polyglutamine-mediated mobility shift. Full-length htt as well as normal and expanded fragments cleaved at amino acid 552 (upper band per allele) or amino acid 513 (lower band per allele) are detected with BKP1 (left panel). Htt552 recognizes only htt cleaved at amino acid 552 with normal and expanded polyglutamine (center panel). 1C2 detects both caspase cleavage products generated from the expanded human htt transgene in the context of murine brain. Faint immunoreactivity to intact expanded htt is also evident (left panel).