Fig. 1.
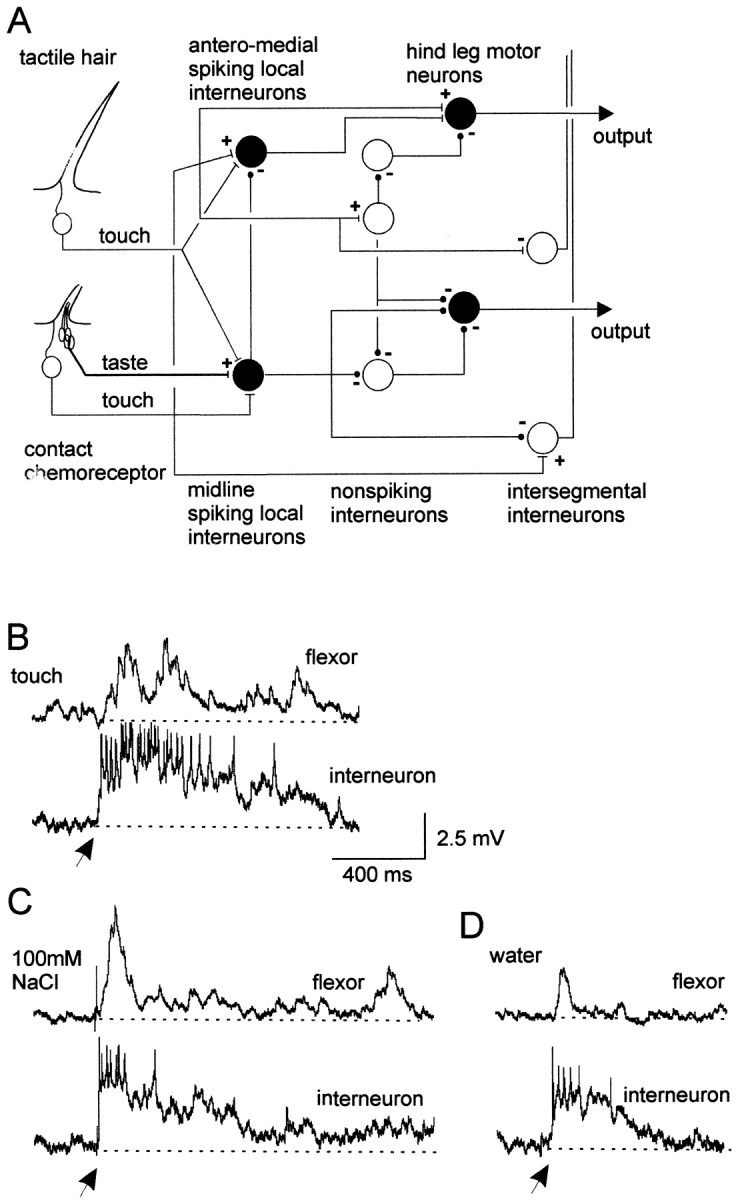
Spiking local interneurons and hindleg motor neurons receive convergent mechanosensory and chemosensory inputs.A, Summary of the basic organization of chemosensory and mechanosensory processing pathways in local circuits. Cell types recorded are shown in black.B, Simultaneous dual recording of a midline spiking local interneuron and a posterior flexor tibia motor neuron. Gently deflecting receptors on a hindleg with a paint brush elicited a sustained depolarization and spikes in an interneuron and depolarizing potentials in a flexor tibia motor neuron. C, Applying a droplet of 100 mm NaCl to the leg also elicited a sustained depolarization and spikes in the same interneuron and a long-lasting depolarization in the same flexor tibia motor neuron. D, A droplet of water applied to the same site on the hindleg evoked briefer depolarizing responses in both neurons. All recordings are from the same pair of neurons. Arrows indicate onset of droplets. In this and subsequent figures of intracellular recordings, thedotted lines represent the membrane potential before stimulation. Flexor, Flexor tibia motor neuron;interneuron, spiking local interneuron of a ventral midline population.
