Fig. 1.
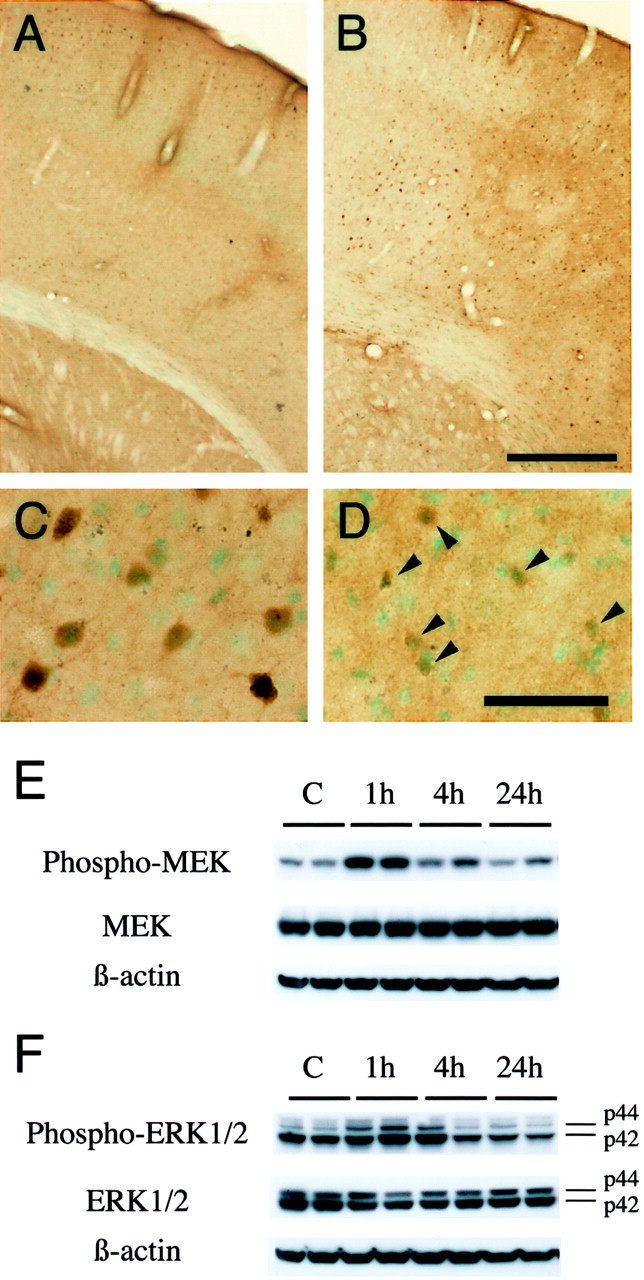
A–D, Phospho-ERK1/2 immunostaining with methyl green counterstaining in coronal brain sections from wild-type mice after transient FCI. Phospho-ERK1/2 was predominantly expressed in the surface layer of the normal mouse brain cortex (A) and was prominently increased 1 hr after reperfusion in the ischemic cortex of the MCA territory (B) but not in the caudate putamen (ischemic core). C, D, Representative photomicrographs of higher magnification in the MCA territory cortex after ischemia. In the ischemic cortex of the MCA territory, homogeneous cytoplasmic and nuclear immunoreactivity of phospho-ERK1/2 was markedly increased 1 hr after reperfusion (C). At 24 hr of reperfusion, the expression of phospho-ERK1/2 was reduced in the ischemic cortex and was primarily accumulated around nuclei (D,arrowheads). In the caudate putamen, phospho-ERK1/2 was hardly seen after 1–24 hr of transient FCI (data not shown). Phospho-ERK1/2 expression in the contralateral hemisphere after reperfusion was not different from that in the normal brain (data not shown). Scale bars: A, B, 400 μm; C, D, 50 μm. E, F, Western blot analysis of phospho-MEK, MEK, phospho-ERK1/2, and ERK1/2 after transient FCI. E, Phospho-MEK, MEK, and β-actin from the whole-cell samples in the nonischemic control brains (lane C) and ischemic brains (lanes 1h–24h). Phospho-MEK and MEK immunoreactivity were evident as a band with a molecular mass of 45 kDa in the whole-cell fraction from the MCA territory cortex of the mouse brains. Phospho- MEK and MEK were expressed constitutively in the nonischemic control brain (lane C). One hour after reperfusion, phospho-MEK was increased significantly compared with the nonischemic controls (top row, lane 1h), whereas it was decreased by 4 hr (top row, lane 4h). MEK showed no prominent increase or decrease after reperfusion in the ischemic cortex (middle row). The results of the β-actin analysis are shown as an internal control (bottom row). F, The bands of phospho-ERK1/2 and ERK1/2 were observed at 44 kDa (ERK1) and 42 kDa (ERK2) in the whole-cell fraction from the MCA territory cortex of the mouse brains. Phospho-ERK1 was increased significantly 1 hr after transient FCI (top row, p44, lane 1h), whereas it returned to the control level by 4 hr (top row, p44, lane 4h). In contrast, phospho-ERK2 was decreased after reperfusion (top row, p42). ERK1/2 did not show prominent changes before or after FCI (middle row). β-actin was used as an internal control, and no difference was observed between the samples (bottom row). Densitometric analysis showed that phospho-MEK was increased significantly 1 hr after reperfusion compared with the nonischemic controls (p < 0.005) and that phospho-ERK1 was increased significantly 1 hr after reperfusion compared with the nonischemic controls (p < 0.005). Phospho-ERK2 was decreased after ischemia, and the decrease was significant at 24 hr compared with the nonischemic control (p < 0.01).
