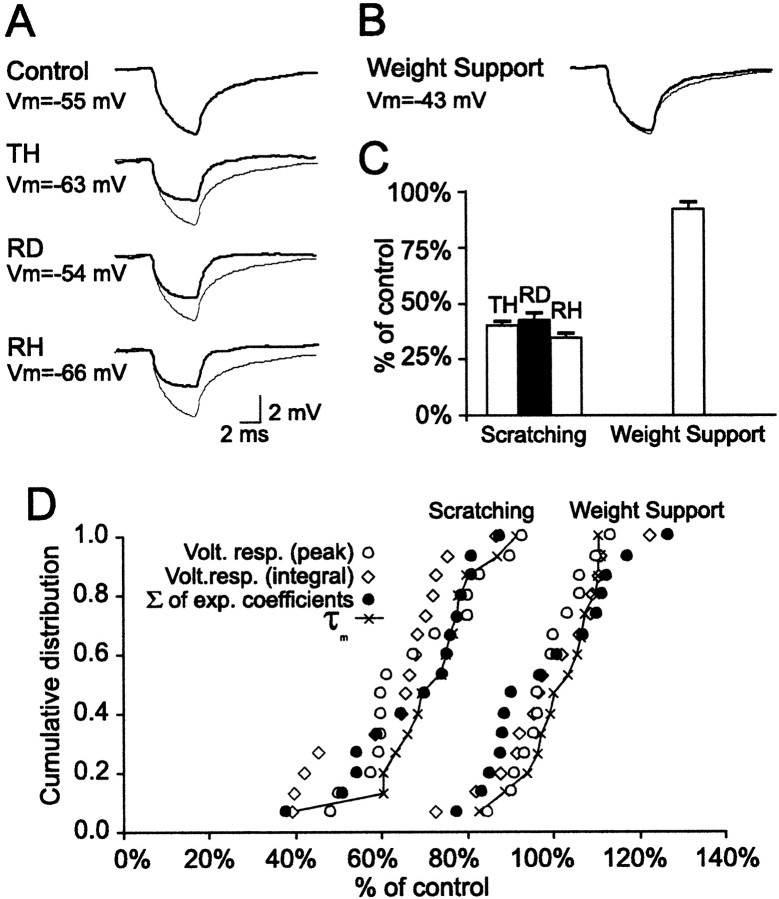
Fig. 2.
Differential change in input resistance during fictive scratching and weight support. A,B, Trace averages (18–54 sweeps) of the voltage deflections produced in an LGS2 motoneuron by short hyperpolarizing current pulses (−4 nA, 5 msec) at rest (top control trace in A), during the three phases of scratching (bottom three traces in A), and during weight support (B). To facilitate comparisons, the control trace was superimposed (thin trace). The time and voltage scales in A are valid also in B. C, Normalized, average changes in input resistance as calculated with the integral method during the TH, RD, and RH phases of scratching and during weight support. D, Cumulative distributions of the changes in input resistance and membrane time constant during both fictive scratching (average across all phases) and weight support (both of the measurements with negative and positive current pulses are included). The values for each method used to estimate the changes in input resistance and for τm were plotted in increasing order. The correlations between the different measurements were strong during both fictive scratching (r = 0.88 integral vs peak; r = 0.96 integral vs Σ of exp coefficients; and r = 0.91 integral vs τm) and weight support (r = 0.98 integral vs peak; r = 0.97 integral vs Σ of exp coefficients; and r = 0.97 integral vs τm).