Fig. 2.
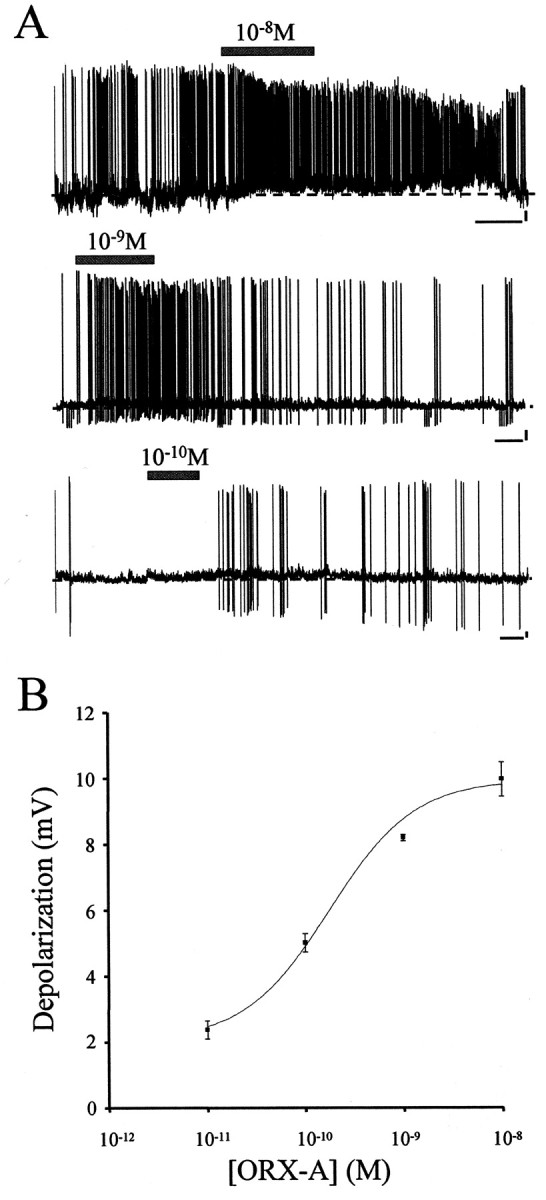
ORX-A depolarizes AP neurons. A, Bath application of various concentrations (10−8 to 10−11m) of ORX-A depolarized 68.8% (33 of 48) of the AP neurons tested. During exposure to ORX-A from a control bath aCSF, AP neurons exhibited rapid sustained depolarizations accompanied in most cases by a rapid increase in firing frequency of action potentials. After washout of ORX-A and replacement of the bath solution with control aCSF, the membrane potential and action potential frequency returned to the control level. ORX-A application is represented by the horizontal bar above each trace. Calibration: 60 sec, 10 mV. The dashed line indicates the baseline of potentials. B, Depolarization of AP neurons by ORX-A is concentration dependent. Changes in membrane potential measured during responses to 10−11 (n = 5), 10−10 (n = 14), 10−9 (n = 4), and 10−8 (n = 10) mextracellular ORX-A were plotted against bath ORX-A concentrations. Data change presented as mean ± SEM data was fitted to a sigmoid concentration–response function, and the corresponding curve was overlaid; EC50 = 1.76 × 10−10m.
