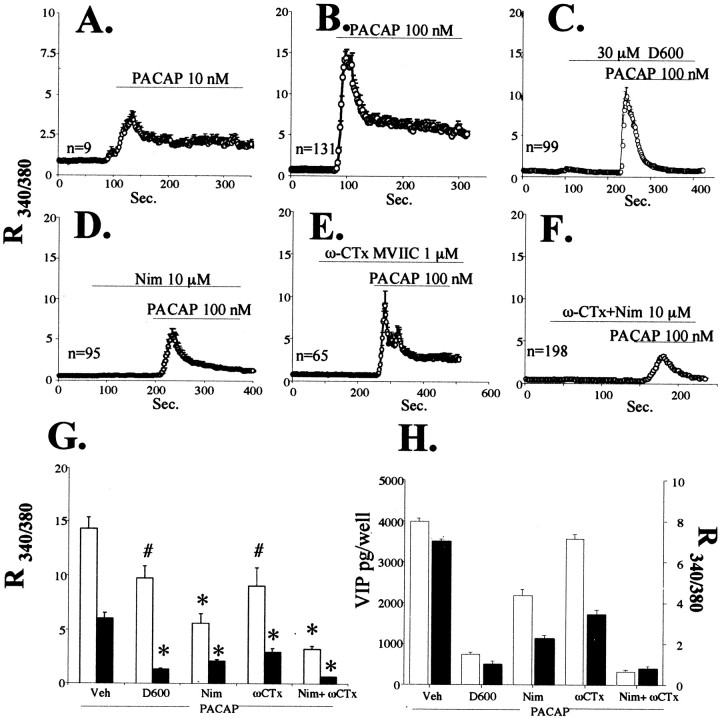
Fig. 5.
Effects of L- and P/N/Q-type voltage-sensitive calcium channel blockade on PACAP-induced calcium elevation and VIP peptide elevation.A–F, Elevation in intracellular calcium elicited by 10 or 100 nm PACAP in the presence of D600, nimodipine, ω-conotoxin MVIIC, or combined ω-conotoxin and nimodipine. Drugs were added as indicated to the perfusion chamber over glass-coverslipped bovine chromaffin cells (as described in Materials and Methods) at 10 or 100 nm PACAP-27, 30 μmD600, 10 μm nimodipine (Nim), or 1 μm ω-conotoxin MVIIC (ω-CTx).G, Comparison of peak versus plateau calcium ratios of treatments in B–F. Data represent means of peaks (white bars) or plateaus (black bars). All comparisons are relative to PACAP alone. *Different from PACAP; p < 0.0001; # different from PACAP; p < 0.01. H, Comparison between inhibition of VIP induction, and inhibition of the plateau phase of calcium elevation, by calcium channel blockade. VIP induction (picograms per well) is shown with white bars, and cytosolic calcium levels during the plateau phase (as the R340/380 ratio, taken from data depicted inA–E) are shown as black bars.