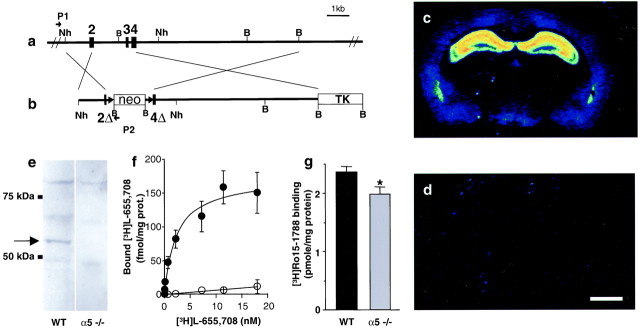
Fig. 1.
Generation and validation of α5 −/− mice.a, b, Schematic representation of the WT α5 allele of the GABAA receptor and the targeting vector, respectively.2, 3,4, Exons 2, 3, and 4; 2Δ,4Δ, partial deletion of exons 2 and 4; neo, neomycin resistance gene;TK, thymidine kinase gene; Nh,NheI restriction site; B,BamHI restriction site; P1,P2, PCR primers. c–g, Pharmacological and biochemical characterization of α5-deficient mice. c, d, Color-coded autoradiograms for [3H]L-655,708 binding to mouse brain sections reveals binding to the hippocampus in the WT (c) and absence of signal in the α5 −/− mice (d). Scale bar, 1 mm. e, Western blot shows the absence of a specific α5 subunit band at 55 kDa in membranes from α5 −/− hippocampus. f, Saturation experiment demonstrating the absence of high-affinity [3H]L-655,708 binding sites in α5 −/− mice (open circles) compared with WT mice (closed circles). g, Total number of [3H] BZ sites labeled by [3H]Ro15–1788 is reduced (−16%) in α5 −/− mice compared with WT controls.