Fig. 3.
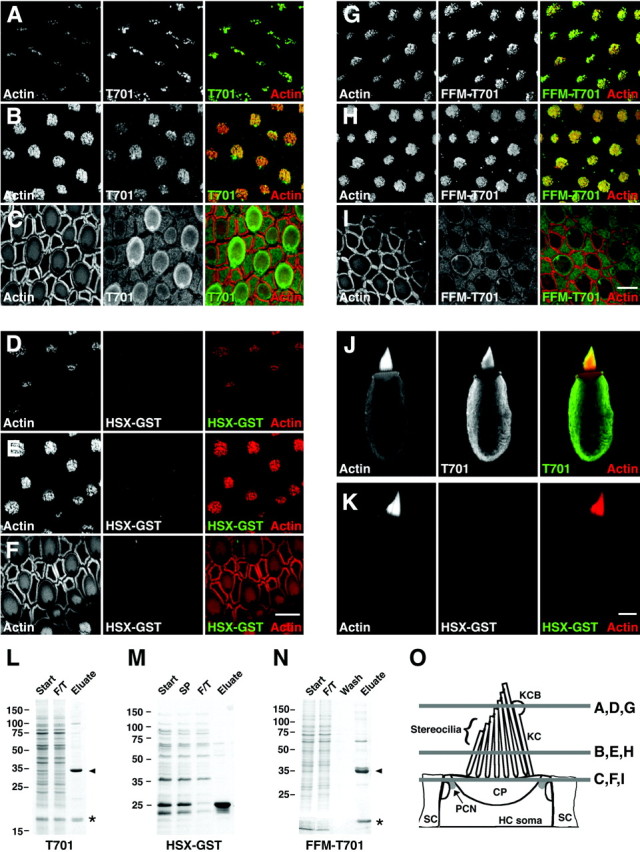
Binding of Myo1c-calmodulin probes to hair-cell receptors. A–I, Left columns, Actin (phalloidin); middlecolumns, epitope-tagged Myo1c or control probe; right columns, combined actin (red) and receptors (green). A–C, T701 binding at stereociliary tips, stereociliary shafts, and pericuticular necklace, respectively. D–F, HSX-GST (negative control) binding at stereociliary tips, stereociliary shafts, and pericuticular necklace, respectively. G–I, Binding of FFM-T701 to hair-cell receptors at stereociliary tips, stereociliary shafts, and pericuticular necklace, respectively. Pericuticular necklace binding is reduced in this particular sample. J, Labeling of isolated hair cell with T701. This cell did not have an intact kinocilium. K, Labeling of an isolated hair cell with HSX-GST. L–N, Coomassie blue-stained SDS-PAGE gels of purified T701, HSX-GST, and FFM-T701. Start, Starting material; SP, soluble proteins;F/T, column flow through; Wash, column wash; Eluate, column eluate. Arrowhead, Myo1c fragments; asterisk, copurifying calmodulin.O, Locations of saccular confocal cross sections shown in A–I. KCB, Kinociliary bulb;KC, kinocilium; HC, hair cell;SC, supporting cell; CP, cuticular plate;PCN, pericuticular necklace. Scale bars: 10 μm (F applies to A–F; Iapplies to G–I; K applies toJ, K).
