Fig. 1.
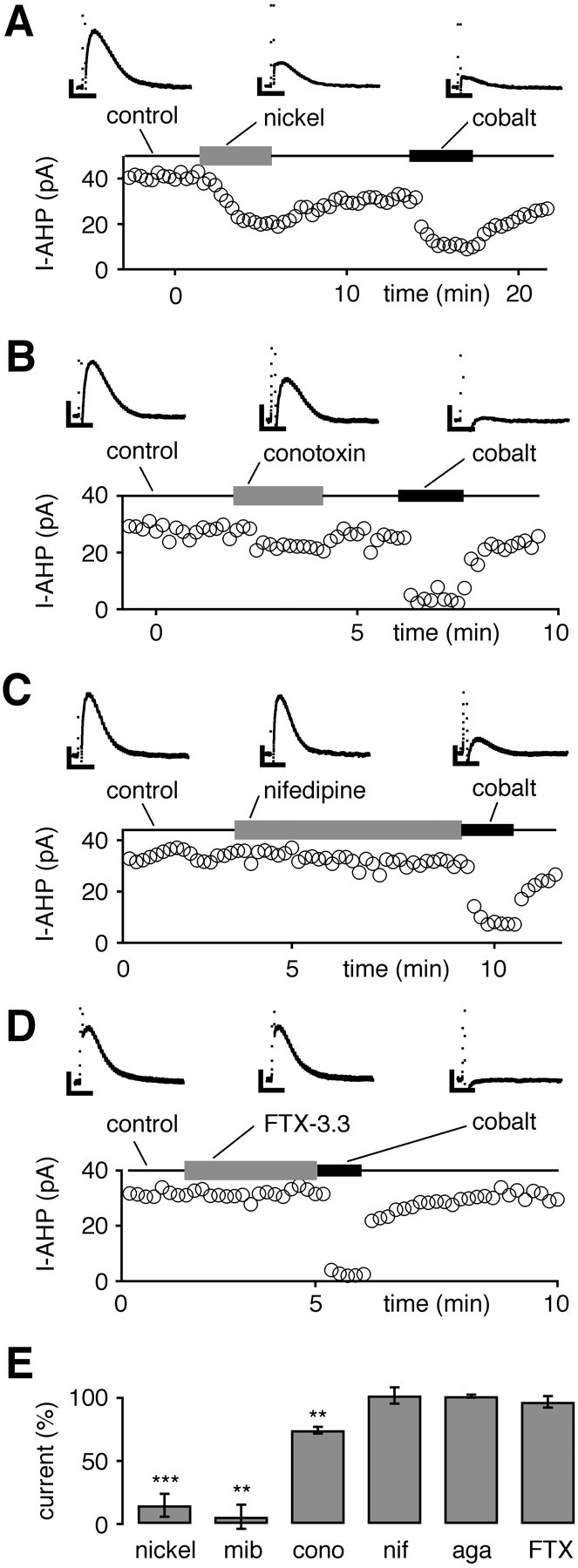
Sensitivity of hybrid-clamp-evoked SK channel-mediated AHP currents (I-AHP) to inhibitors of Cav channels recorded in the perforated whole-cell configuration. A, Low micromolar concentrations (100 μm) of nickel (T-type) reversibly inhibited most of the cobalt-sensitive I-AHP. B, ω-Conotoxin-GVIA (conotoxin; 1 μm) reversibly reduced a minor part of the cobalt-sensitive I-AHP. C, Nifedipine (10 μm) did not affect I-AHPs.D, FTX-3.3 (1 μm) had no effect on I-AHPs.E, The summary of experiments in A–Dshows that cobalt-sensitive I-AHPs were activated preferentially via calcium channels sensitive to low micromolar nickel (100 μm; 85 ± 9%; n = 13; ∗∗∗p < 0.0005) and mibefradil (mib; 10 μm; 94 ± 10%; n = 6; ∗∗p < 0.005), whereas only a small component was sensitive to 1 μm ω-conotoxin-GVIA (cono; 26 ± 3%; n = 4; ∗∗p < 0.005). Nifedipine (nif; 10 μm) did not affect I-AHPs (residual current, 102 ± 6%; n = 6; p > 0.05). Similarly, 1 μm FTX-3.3 (FTX; residual current, 97 ± 5%; n = 5; p > 0.05) and 0.1 μm agatoxin-TK (aga; residual current, 101 ± 1%; n = 3; p > 0.05) had no effect on I-AHPs. Current amplitudes were normalized to cobalt-sensitive I-AHP in each individual experiment except for mibefradil, in which the mean value of cobalt block was used (1 mm; residual current, 29 ± 4%; n= 29). Calibration: A–D, 0.2 sec, 10 pA.
