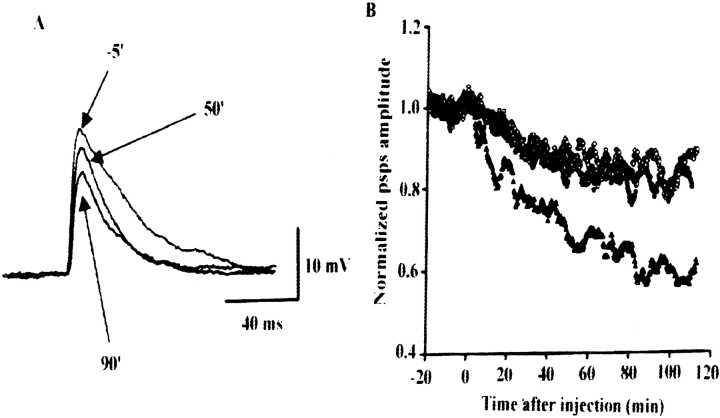
Fig. 10.
Activity-dependent inhibition of synaptic transmission by the CaMKII-binding domain of syntaxin-1A in cultured SCG neurons. A, Syntaxin [145–184] was introduced into presynaptic neurons by diffusion from a pipette from the start of membrane disruption by suction at t = 0.B, EPSPs of neurons microinjected with the CaMKII-binding fragment were significantly lower than those of neurons microinjected with deletion mutant that was unable to bind CaMKII. Normalized average EPSPs were plotted from five experiments with syntaxin [145–184] (CaMKII-binding fragment;triangles) and with syntaxin [152–184] (fragment unable to bind CaMKII; Fig. 3A; circles). CaMKII-binding fragments of NR2A ([1389–1461];diamonds) and NR2B ([1290–1309];squares) glutamate receptors were also microinjected (Strack et al., 2000; Gardoni et al., 2001). EPSP amplitudes at 80 min after the start of injection with syntaxin [145–184] and syntaxin [152–184] were −39 ± 7.0% (n = 5; mean ± SEM) and −14 ± 5.8% (n = 5), respectively. psps, Postsynaptic potentials.