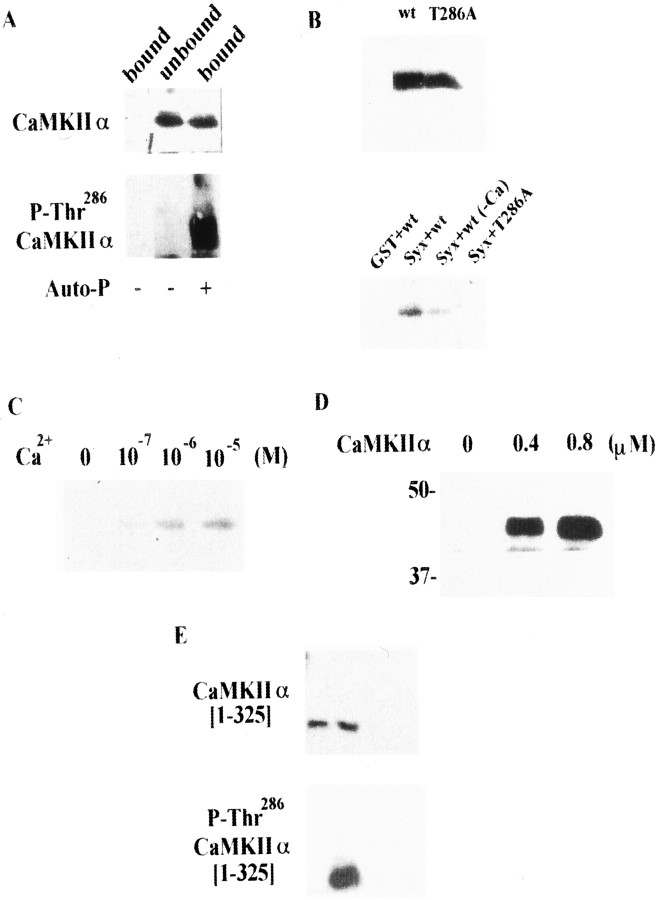
Fig. 2.
CaMKII binds to syntaxin only when autophosphorylated. A, Purified CaMKIIα also binds syntaxin after autophosphorylation. The fraction unbound to GST–syntaxin after re-autophosphorylation was not recognized by anti-autophosphorylated CaMKII antibody. CaMKIIα (5 μg) purified from rat brain was autophosphorylated (Auto-P) in buffer containing 50 mm HEPES-NaOH, pH 8.0, 8 mmMg(CH3COO)2, 0.25 mmCaCl2, 2 μm CaM, and 0.5 mm ATP for 5 min at 30°C, and then incubated with immobilized GST or GST–syntaxin (4 nmol) for 1 hr at 4°C. After centrifugation, the supernatant was collected as the unbound fraction. The PreScission protease fraction was collected as the bound fraction. Samples were resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted using anti-CaMKIIα mAb or anti-autophosphorylated CaMKII mAb.B, T286A-CaMKIIα could not bind syntaxin.Top, Both wild-type CaMKIIα (wt) and T286A-CaMKIIα (T286A) were produced by in vitro translation. Bottom, Only wt CaMKIIα bound to syntaxin in the pull-down study in presence of Ca2+/ATP. The cDNA encoding rat CaMKIIα or T286A-CaMKIIα (provided by Dr. H. Schulman) was added to thein vitro translation kit (Promega). Proteins were expressed by incubating kit components for 1.5 hr at 30°C and then adding immobilized GST–syntaxin as above. After elution with SDS sample buffer, bound proteins were blotted and detected using streptavidin-conjugated alkaline phosphatase. C, CaMKIIα produced using in vitro translation also shows Ca2+ sensitivity for binding to syntaxin after autophosphorylation. Translation in vitro proceeded as described above, and CaMKIIα was autophosphorylated in buffer containing Tris-HCl, pH 7.6, 0.5 mmCaCl2, 2 μm CaM, 2 mmMgCl2, and 0.5 mm ATP at 30°C for 15 min. The autophosphorylated CaMKIIα was incubated with immobilized GST–syntaxin (4 nmol) at 4°C for 1 hr and then with binding buffer containing various concentrations of Ca2+ for an additional 1 hr. D, Dose-dependent binding of CaMKII to syntaxin. GST–syntaxin (4 nmol) was incubated with recombinant CaMKIIα at various concentrations. E, CaMKIIα lacking the association domain [1–325] (i.e., monomeric CaMKII) does not bind to syntaxin, even when autophosphorylated. The monomeric CaMKIIα was autophosphorylated and incubated with the immobilized GST–syntaxin as described above (A).