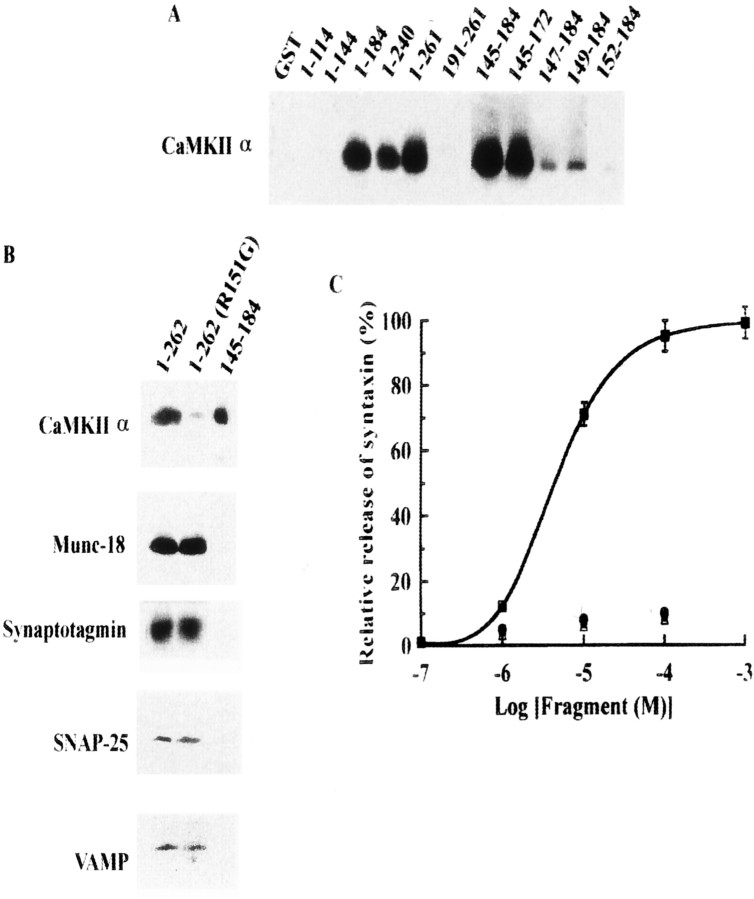
Fig. 4.
Determination of CaMKIIα-binding site in syntaxin. A, Binding visualized using anti-CaMKII antibody. Each recombinant fragment derived from syntaxin 1A as a GST-fusion protein (4 nmol) was immobilized to glutathione Sepharose, incubated with autophosphorylated purified CaMKIIα (5 μg), and then cleaved by PreScission protease like the brain S2 fraction (see legend to Fig. 1). Eluted fractions were resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted against anti-CaMKIIα mAb. B, R151G is critical to binding of CaMKII to syntaxin, but mutation in this amino acid did not affect interactions between syntaxin and other syntaxin-binding proteins. Each GST-fusion protein was immobilized as well as those described in A and incubated with each recombinant protein (1 nmol) or with CaMKIIα (5 μg). After PreScission protease digestion, eluted proteins were resolved by 15% SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted. C, Dissociation of CaMKII from syntaxin by CaMKII-binding fragments derived from syntaxin 1A ([145–184]; squares) and glutamate receptors of NR2A ([1349–1461]; circles) and NR2B ([1290–1309];triangles). GST–syntaxin 1A [1–262] (4 nmol) was immobilized with glutathione Sepharose and then incubated with purified autophosphorylated CaMKII (5 μg). After rinsing with PBS, immobilized syntaxin–CaMKII complex was incubated with syntaxin [145–184] for 1 hr at 4°C and centrifuged. In some experiments, various concentrations of NR2A or NR2B fragments were incubated with immobilized syntaxin–CaMKII complex as described above. The supernatant containing released CaMKII was resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted against anti-CaMKIIα mAb. The amount of the bound CaMKII before incubation with syntaxin fragments [145–184] or derived from glutamate receptors is designated as 100%.