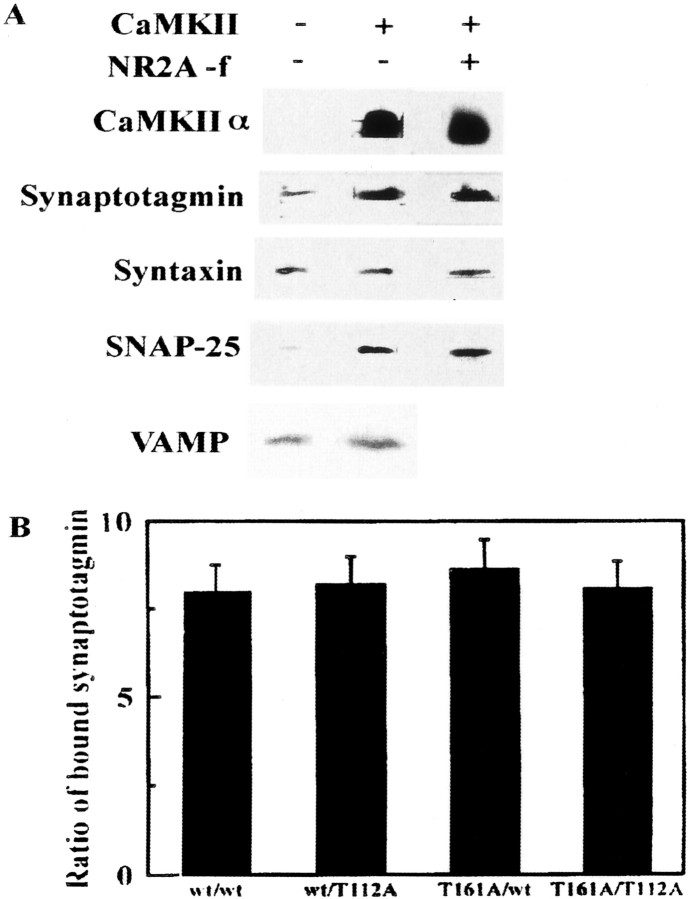
Fig. 7.
In vitro reconstitution of the syntaxin 1A–CaMKII complex with other presynaptic proteins.A, Syntaxin–CaMKII complexes formed in vitro recruited more synaptotagmin and SNAP-25 than syntaxin alone. After the formation of CaMKII–syntaxin complex with synaptotagmin I and SNAP-25, NR2A [1389–1464] (10−5m) was added in some experiments to a complex composed of those four proteins for 1 hr.B, Relative binding of synaptotagmin I to syntaxin binding in the absence or presence of CaMKII. Combinations were as follows: wt/wt, Wild-type syntaxin/wild-type synaptotagmin I; wt/T112A, wild-type syntaxin/T112A–synaptotagmin I; T161A/wt, T161A–syntaxin/wild-type synaptotagmin I; andT161A/T112A, T161A–syntaxin/T112A–synaptotagmin I. T112A–synaptotagmin I, a mutant without a CaMKII-dependent phosphorylation site, binds to syntaxin 1A in a manner similar to wild type in the presence of CaMKII. Binding was quantified by densitometry of immunoblots. The ratio was calculated as amount of syntaxin-bound synaptotagmin I in the presence of CaMKII compared with that in the absence of CaMKII.