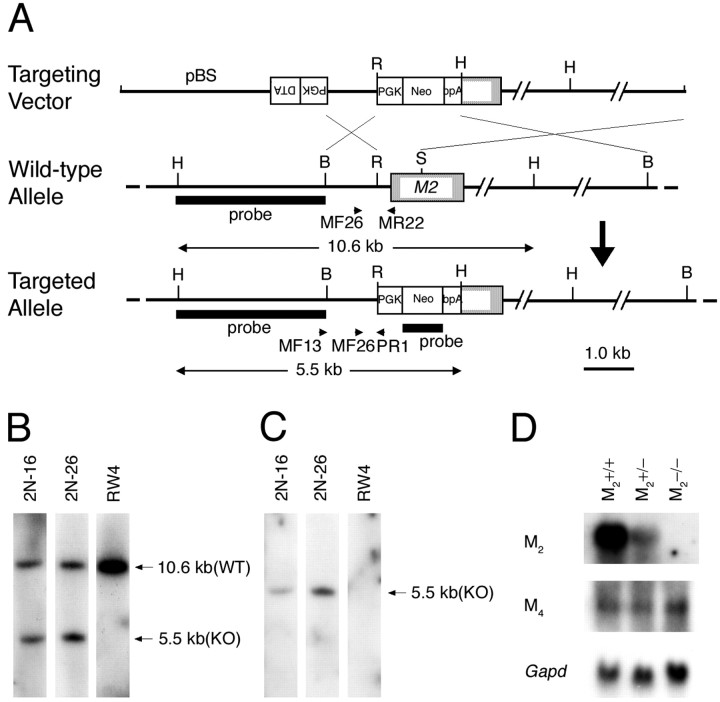
Fig. 1.
Generation of M2−/− mice.A, Targeting strategy. Arrows MF13 andPR1 indicate the PCR primers used for homologous recombinant screening, and arrows MF26,MR22, and PR1 indicate PCR primers used for genotyping. BamHI (B),HindIII (H),EcoRI (R), and SmaI (S) sites relevant to the identification of homologous recombinant clones are shown together with the expected sizes hybridizable to the M2 and the neoprobes. B, Hybridization with the M2 probe showing a 5.5 kb band specific to the targeted allele (KO) and a 10.6 kb band derived from the wild-type allele (WT). C, Hybridization with the neo probe showing a 5.5 kb band specific to the targeted allele. D, Northern analysis showing mRNA levels of M2 and M4 in the brains of wild-type, M2+/−, and M2−/− mice. Note that the M2 mRNA in the M2+/− brain decreased to approximately half of the wild-type brain and was absent in the M2−/− brain. The mRNA levels of M4 are not different among the three genotypes. Bottom, Signals hybridized with a Gapd probe used as an internal control.