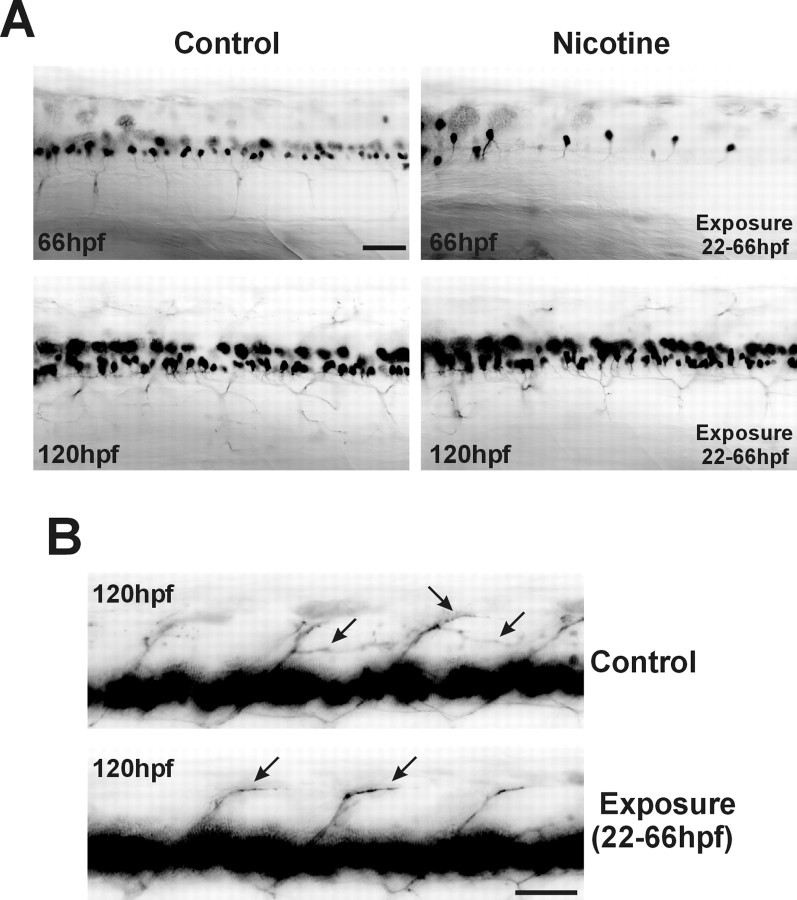
Fig. 4.
Nicotine-mediated delay in motoneuron GFP expression in 66 hpf embryos. Photomicrographs fromislet-1 GFP transgenic embryos are shown.A, In vivo GFP imaging of the rostral spinal cord of control embryos at both 66 and 120 hpf, a 66 hpf embryo exposed to 33 μm nicotine from 22 to 66 hpf, and a 120 hpf embryo exposed to 33 μm nicotine from 22 to 66 hpf and then returned to embryo medium until 120 hpf. B, Photomicrographs of caudal spinal cord. Arrows indicate dorsal secondary motoneuron axons expressing GFP from a 120 hpf control embryo and a 120 hpf embryo that was exposed to 33 μmnicotine between 22 and 66 hpf. For imaging, the exposure time was adjusted to detect GFP in the axons. Such exposure times caused the GFP signal in the spinal cords to be saturated (continuous black). Scale bars, 40 μm.