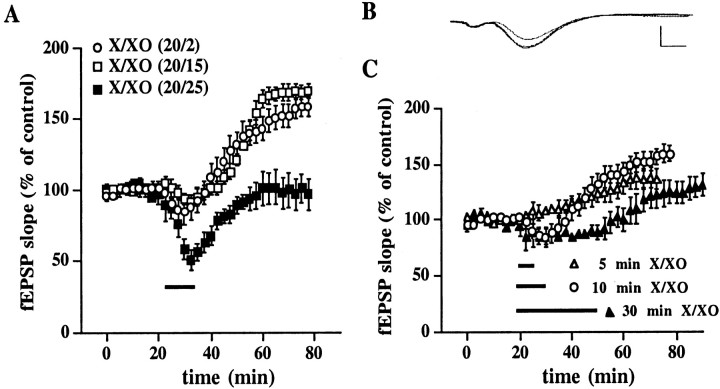
Fig. 1.
X/XO-induced potentiation is concentration- and time-dependent. A, X/XO-induced potentiation is dependent on the concentration of superoxide. Stable baseline responses of the fEPSP slope were recorded in hippocampal area CA1 for 20 min before the addition of X/XO (indicated by the bar) for 10 min. X concentrations were kept constant at 20 μg/ml for all experiments. XO concentrations were 2 μg/ml (open circles, n = 10), 15 μg/ml (open squares, n = 8), or 25 μg/ml (filled squares, n = 6). These X/XO concentrations produced superoxide concentrations of 1–5, 10, and 50 μm, respectively. Error bars indicate SEM for the indicated number of determinations. When we compared the fEPSP slope 45 min after the washout of X/XO with the fEPSP slope immediately before the addition of X/XO, statistically significant potentiation was observed for XO concentrations of 2 and 15 μg/ml (p < 0.001 by paired Student'st test). B, Representative fEPSPs before, 30 min after, and 45 min after treatment with X/XO (20 and 2 μg/ml). Calibration: 2 mV, 3 msec. C, X/XO-induced potentiation is dependent on the duration of X/XO incubation. Stable baseline responses were recorded for 20 min before the addition of X/XO (20 and 2 μg/ml) for 5 (open triangles, n= 4), 10 (open circles, n = 10), or 30 (filled triangles, n = 4) min as indicated by the bars. Error bars are SEM for the indicated number of determinations. When we compared the fEPSP slope 45 min after the washout of X/XO with the fEPSP slope immediately before the addition of X/XO, statistically significant potentiation was observed for the 5 and 10 min X/XO incubations (p < 0.01 and 0.001, respectively, by paired Student's t test).