Fig. 2.
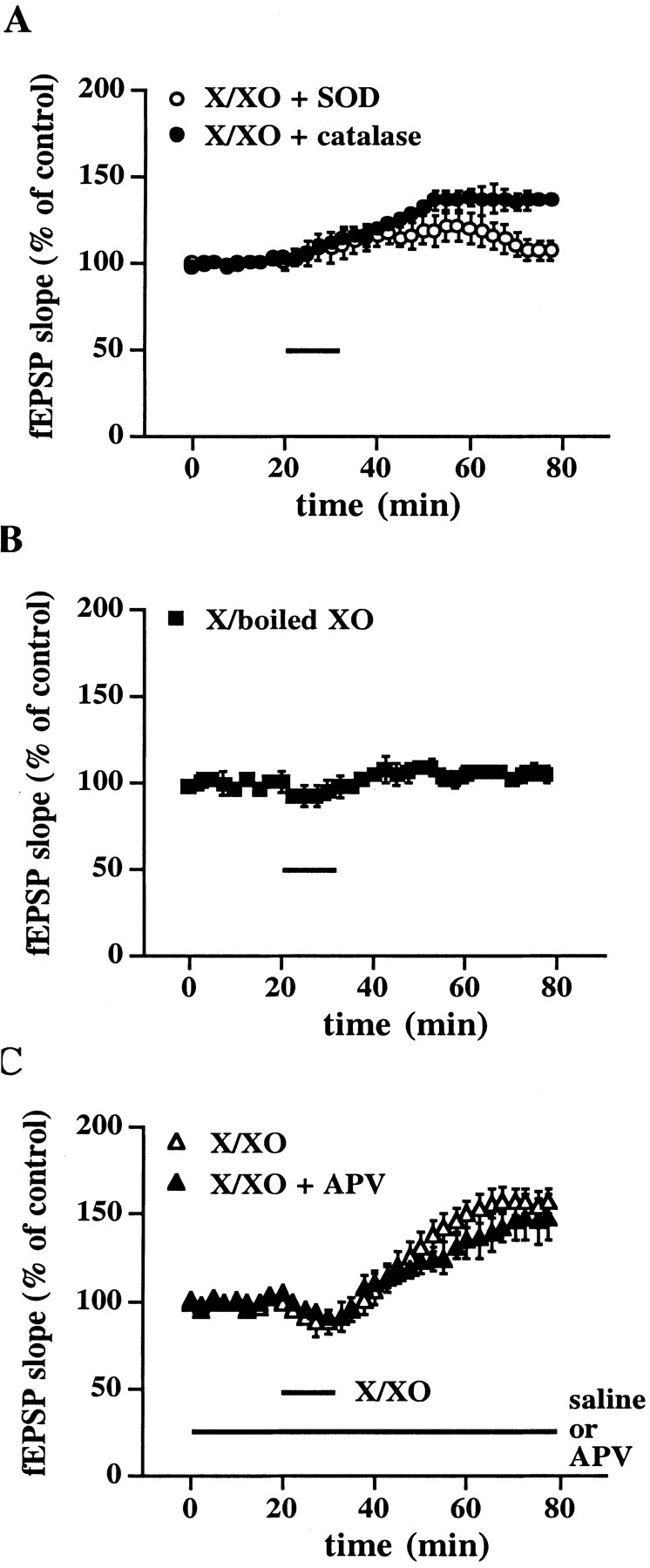
Characterization of X/XO-induced potentiation.A, X/XO-induced potentiation is superoxide-dependent. Stable baseline responses were recorded for 20 min before the slices were incubated with X/XO and antioxidant enzymes for 10 min (indicated by the bar). Open circles are ensemble averages from slices incubated with X/XO (20 and 2 μg/ml) and SOD (25 μg/ml). Filledcircles are ensemble averages from slices incubated with X/XO and catalase (25 μg/ml). Error bars are SEM for eight determinations. When we compared the fEPSP slope 45 min after the washout of X/XO with the fEPSP slope immediately before the addition of X/XO, statistically significant potentiation was observed in the presence of catalase (p < 0.001). B, Specificity of X/XO-induced potentiation.Filled squares are ensemble averages from slices incubated with X (20 μg/ml) and boiled XO (2 μg/ml). Error bars are SEM for eight determinations. C, X/XO-induced potentiation is downstream of NMDA receptor activation. Stable baseline responses were recorded for 20 min before the slices were incubated with X/XO (20 and 2 μg/ml) for 10 min either with (filled triangles) or without (open triangles) the NMDA receptor antagonist APV (50 μm) in the perfusate (indicated by thebars). Error bars are SEM for six determinations. There was no statistically significant difference in the potentiation between the groups 45 min after the washout of X/XO (p > 0.05 by paired Student'st test).
