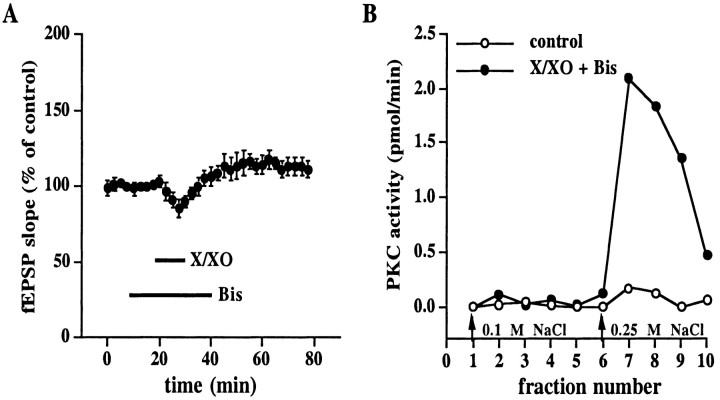
Fig. 5.
Effect of the PKC inhibitor Bis on X/XO-induced potentiation and X/XO-induced increase in autonomous PKC activity.A, X/XO-induced potentiation is PKC-dependent. Stable baseline responses of the fEPSP slope were recorded for 20 min before the slices were incubated with X/XO (20 and 2 μg/ml) for 10 min in the presence of the PKC inhibitor Bis (500 nm) as indicated by the bars. Error bars are SEM for eight determinations. When we compared the fEPSP slope 45 min after the washout of X/XO with the fEPSP slope immediately before the addition of X/XO, no statistically significant potentiation was observed (p > 0.05 by paired Student'st test) B, X/XO-induced persistent increase in autonomous PKC activity is present after the washout of Bis. Slices were incubated with either normal saline (open circles, n = 5) or X/XO (filled circles, n = 5) in the presence of Bis as described in A. At the end of the experiment the slices were frozen and homogenized. The soluble fraction of the homogenates was applied to a DEAE column, and PKC was eluted from the column with either 0.1 or 0.25 m NaCl (arrows). Autonomous PKC activity was measured in each fraction as described in Materials and Methods.