Fig. 4.
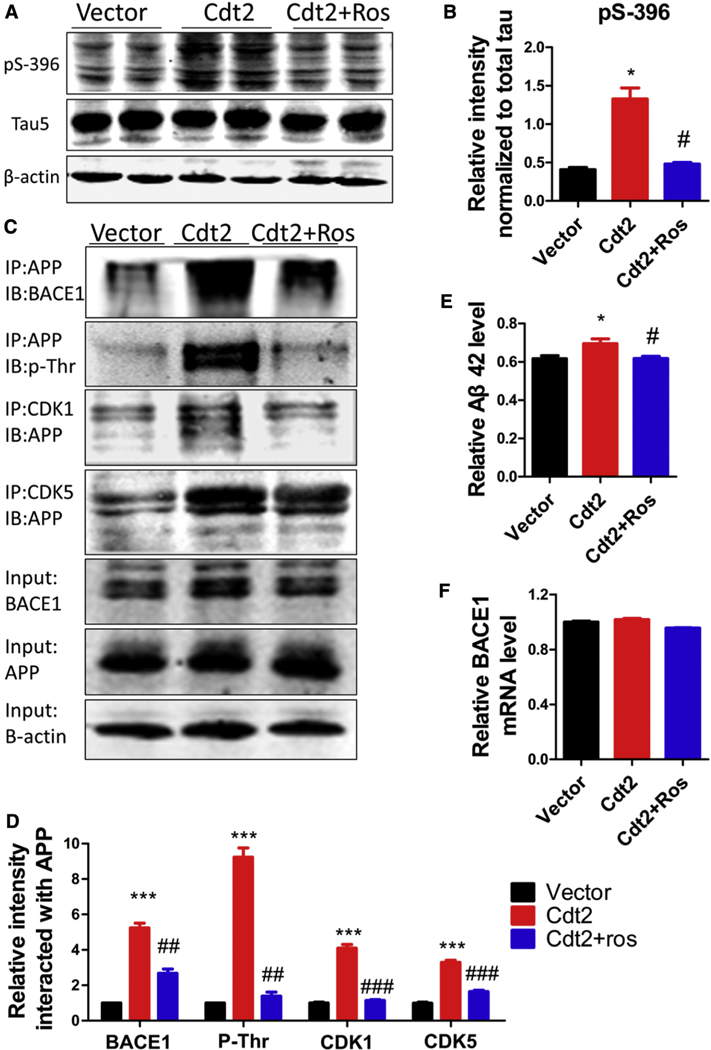
Overexpression of CDT2 induces tau hyperphosphorylation and Aβ overproduction. CDT2 was overexpressed in C57BL/6J mice in vivo via adeno-associated virus (AAV) injection. (A and B) Western blotting and statistical analysis showed the marked increase of tau phosphorylation at Ser396 in CDT2-treated C57BL/6J mice. The CDKs inhibitor roscovitine attenuated tau hyperphosphorylation in CDT2-treated mice, while the level of total tau recognized by Tau5 had no change among each group. (C and D) Transfection with CDT2 in N2a/APP cells induced a significant increase in the interaction of APP with BACE1, CDK1 and CDK5 and APP threonine phosphorylation levels compared with controls. Inhibition of CDKs by roscovitine markedly attenuated the interaction of APP with BACE1, CDK1 and CDK5 and APP threonine phosphorylation levels. (E) The level of Aβ42 was significantly increased in CDT2 mice compared with control animals, while CDKs inhibition by roscovitine restored Aβ42 level to normal. (F) BACE1 mRNA levels did not change among each group. All data represent mean 6 SEM. * P < .05; *** P < .001, versus vector control. # P < .05; ## P < .01; ### P < .001, versus Cdt2.
