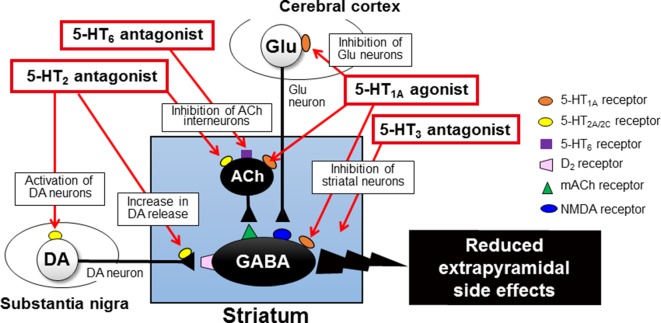
Figure 5.
Mechanisms underlying serotonergic modulation of antipsychotic-induced extrapyramidal side effects (EPS). Activation of 5-HT1A receptors, especially postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors in the striatum and cerebral cortex, alleviates antipsychotic-induced EPS. Blockade of 5-HT2 receptors on nigral dopamine neurons and their nerve terminals in the striatum can relieve the negative serotonergic regulation and thereby can increase the dopaminergic activities, which contributes to EPS reduction. Similarly, blockade of 5-HT3 and 5-HT6 receptors attenuates antipsychotic-induced EPS possibly via acting in the striatum. This figure is quoted and arranged from Biol. Pharm. Bull. 36, 1396, 2013.