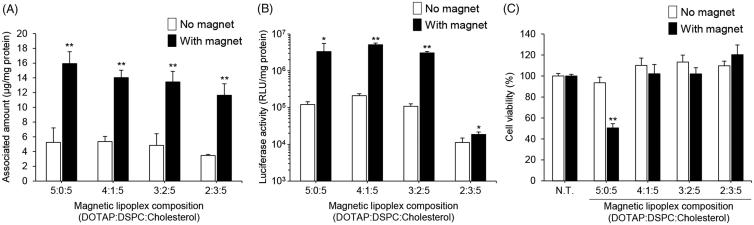
Figure 1.
Effect of the lipid composition of the magnetic cationic liposomes on their cellular association, pDNA transfection efficiency, and cytotoxicity in RAW264 cells. Cellular association and/or uptake of magnetic cationic liposomes (A) and the level of luciferase expression following magnetic lipoplex administration (B). Magnetic lipoplexes prepared using various lipid compositions (DOTAP:DSPC:cholesterol = 5:0:5, 4:1:5, 3:2:5, or 2:3:5) and containing 0.1 mg/mL of SPIONs were added to each well (as 1 µg of pDNA), and incubated for 10 min at 37 °C in the presence or absence of a magnetic field. The mixing ratio of the magnetic cationic liposomes/pDNA was 10:1. Each value represents the mean + SD (n = 4). *p < .05; **p < .01, compared with no magnet. (C) Cell viability of RAW264 cells incubated with magnetic lipoplexes (as 1 µg of pDNA) for 10 min at 37 °C in the presence or absence of a magnetic field. Each value represents the mean + SD (n = 4). **p < .01, compared with non-treated (N.T).