Fig. 1.
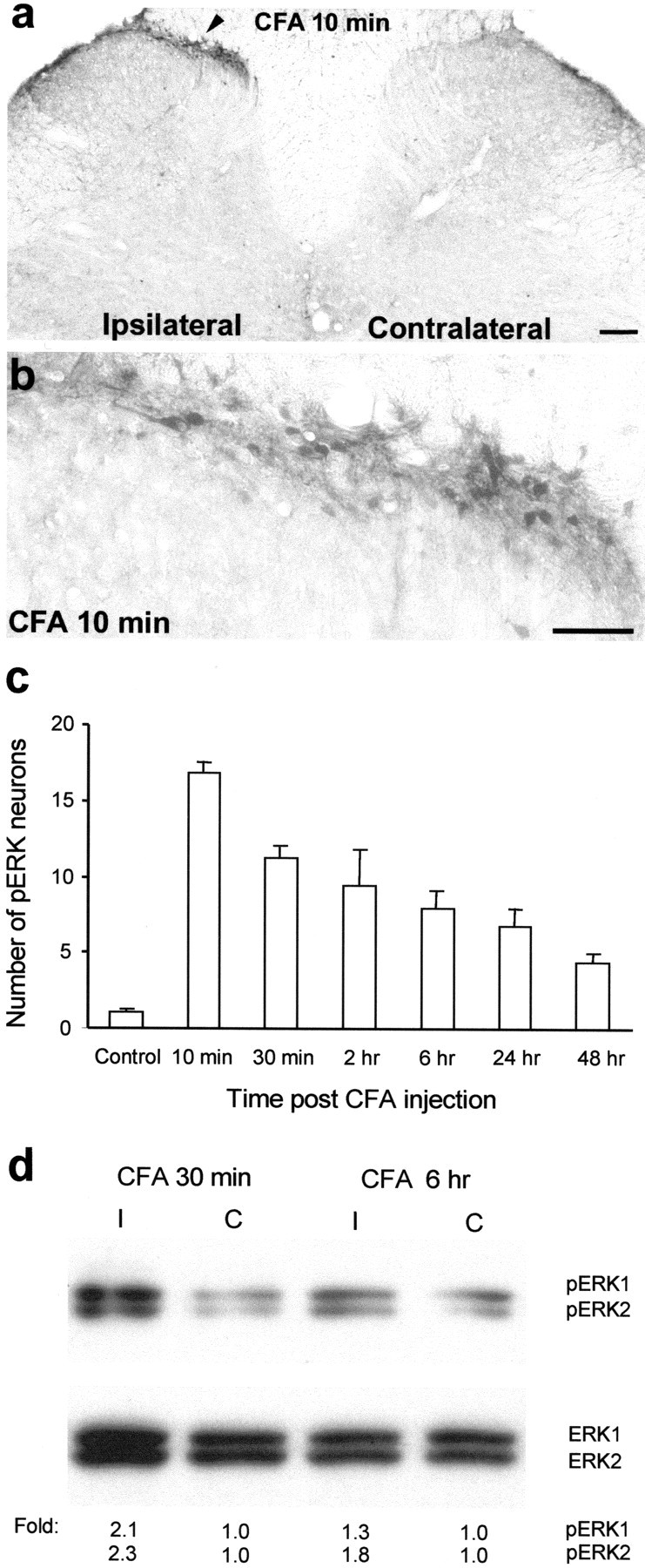
CFA induces a sustained activation of ERK.a, A low-magnification image showing induction of ERK phosphorylation in laminae I–IIo neurons of the ipsilateral spinal cord (indicated with an arrowhead) 10 min after CFA injection into a hindpaw. Scale bar, 200 μm. b, A high-magnification image of a, showing ERK activation in the medial superficial dorsal horn of the ipsilateral spinal cord 10 min after CFA injection. Scale bar, 50 μm. c, Time course of pERK induction after CFA administration measured by the number of pERK-positive neurons in the superficial (I–IIo) layers of the ipsilateral dorsal horn. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). d, Western blot showing increased ERK phosphorylation of both ERK1 (44 kDa) and ERK2 (42 kDa) in the ipsilateral (I) dorsal horn compared with contralateral (C) side, 30 min and 6 hr after CFA injection. The bottom panel indicates levels of total ERK1 and ERK2, as loading controls. Foldrepresents comparative levels over the corresponding contralateral side after normalizing for loading.
