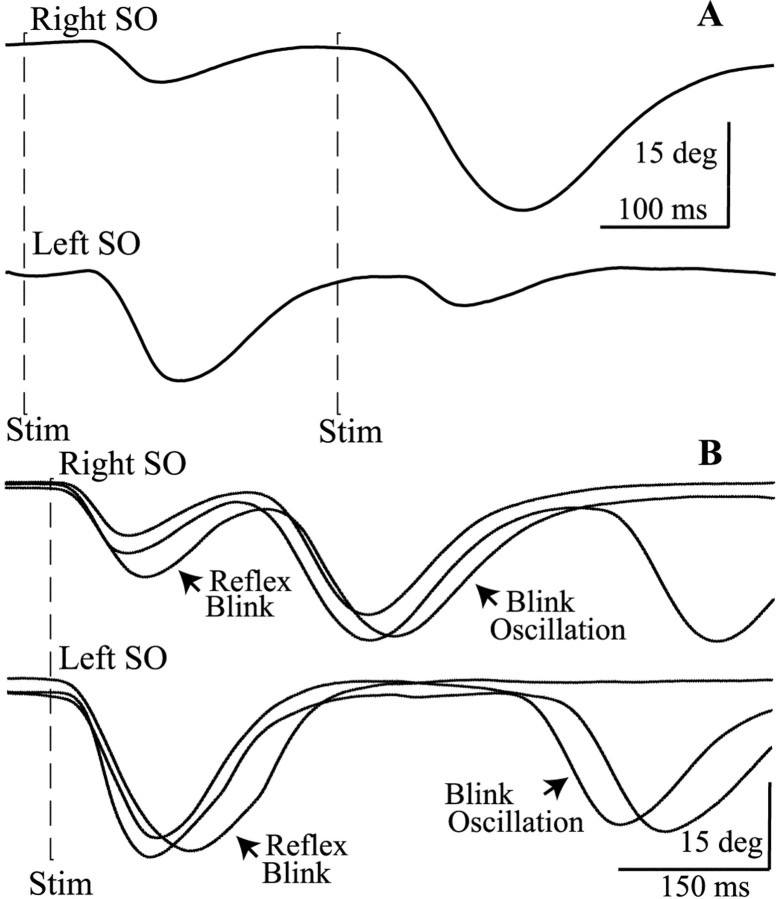
Fig. 4.
Unilateral facial palsy alters trigeminal blinks.A, The relative amplitude of blinks evoked by a 2T SO stimulus (first dashed line Stim) and an identical SO stimulus (second dashed line Stim) occurring 250 msec later are different for stimulation of the SO ipsilateral (Right SO, top trace) or contralateral (Left SO, bottom trace) to the right facial palsy. Each trace is a single trial from the unaffected, left, upper eyelid. B, A single 2T SO stimulus (dashed line Stim) ipsilateral (Right SO, top traces) and contralateral (Left SO, bottom traces) to the facial palsy evokes a reflex blink and additional blinks (Blink Oscillation) that occur at a constant time relative to the onset of the preceding blink. Each trace is a single trial from the unaffected, left, upper eyelid.