Fig. 3.
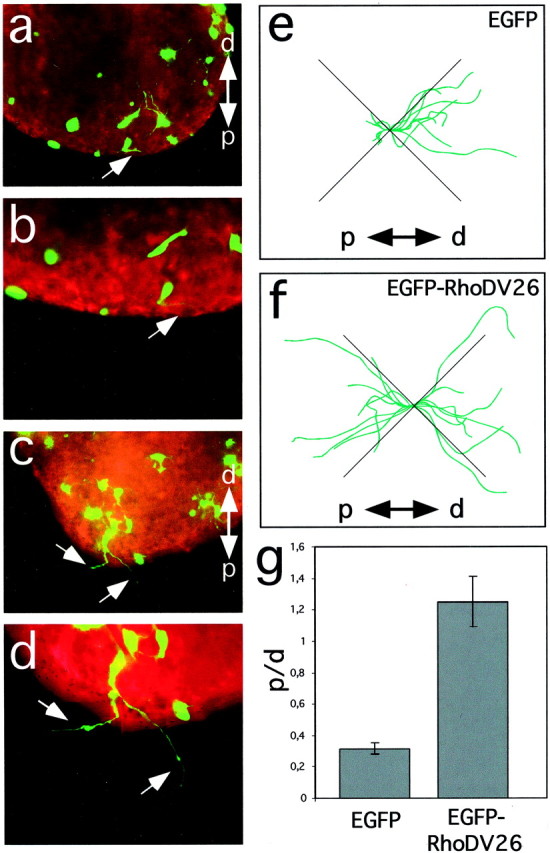
RhoD blocks repulsion of sympathetic axons by Sema3A. Explanted ganglia were transfected by particle-mediated gene transfer with a mixture of ptauEGFP and pEGFP (a,b, e) or pBK-EGFP-RhoDV26 (c, d, f), cultured together with Sema3A-expressing cell aggregates and analyzed after 24 hr of culture by following the trajectories of EGFP-positive axons (arrows). Cell aggregates are located outside the field of view (proximal is to the bottom). Staining with phalloidin–rhodamine confirmed that no EGFP-negative axons were present in the proximal quadrant. Representative images of transfected ganglia are shown. e, f, A camera lucida representation of tauEGFP-positive axons extending into proximal (p) and distal (d) quadrants is shown. Axonal trajectories were recorded from neurons located at the proximal edge of explanted ganglia facing the Sema3A-secreting cell aggregate (n = 6). Axons extending into the lateral quadrants are not informative for their Sema3A sensitivity and were not included in our analysis.g, EGFP-positive axons extending toward (p) or away (d) from the cell aggregates secreting Sema3A were counted, and the ratio of axons growing proximally to that growing distally (p/d ratio) was calculated. Whereas axons extended preferentially away from Sema3A-expressing cells in control transfections, cells transfected with the expression vector for RhoDV26 had axons that extended with similar probability either proximally or distally (n = 6, 20–40 ganglia per experiment).
