Fig. 9.
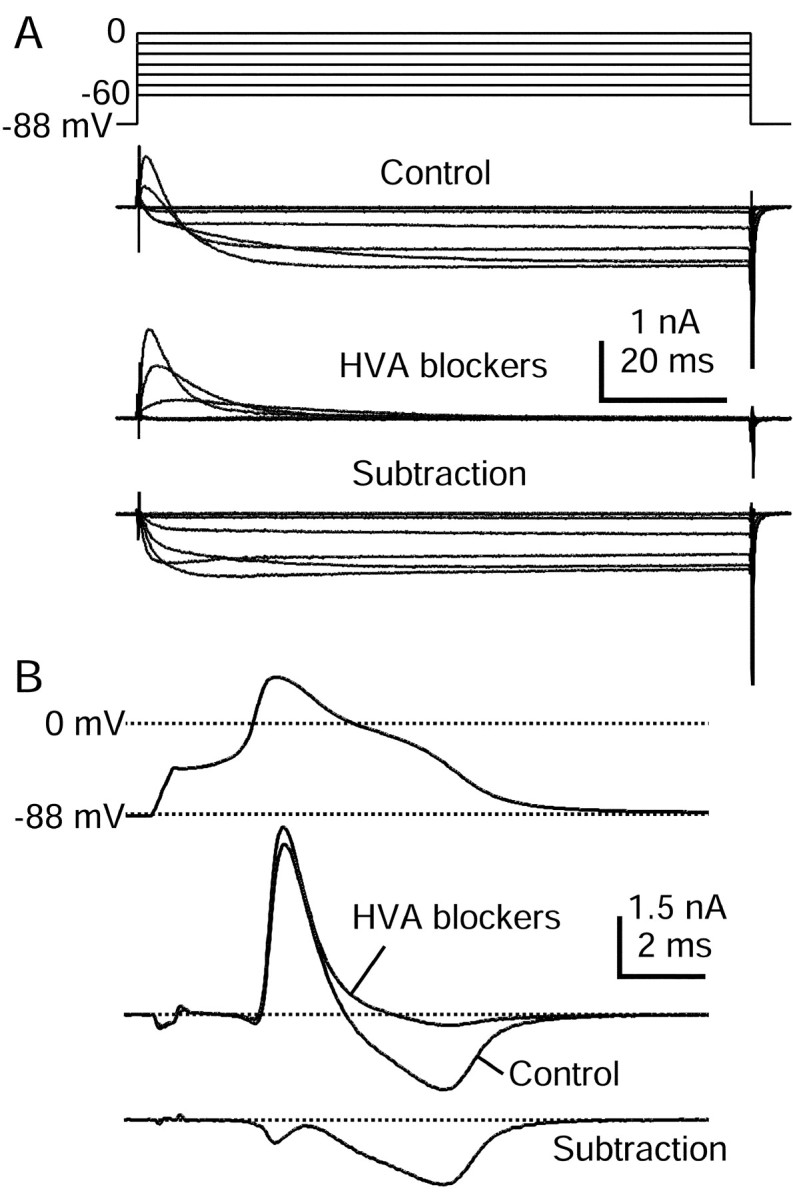
HVA calcium currents elicited by action potential clamp in small DRG cells. A, Currents elicited by step depolarizations in control (top) and then after the application of 10 μm nimodipine, 1 μmω-conotoxin-GVIA, and 250 nm ω-Aga-IVA (middle). Internal solution contained (in mm): 140 K-Mes, 13.5 NaCl, 1.6 MgCl2, 0.09 EGTA, 9 HEPES, 0.9 glucose, 14 Tris-creatine PO4, 4 Mg-ATP, and 0.3 Tris-GTP, pH 7.2 (with KOH). External solution for initial recording of action potential was Tyrode's solution. External solution for recording calcium current contained (in mm): 160 TEA-Cl, 2 CaCl2, 2 MgCl2, and 10 HEPES, pH 7.4. Note outward Na current exiting through TTX-R sodium channels. Subtraction of currents with and without blockers yields the HVA calcium current (bottom). In these traces 120 μsec after the voltage step has been blanked to remove uncompensated capacitive current.B, Subtraction procedure during action potential clamp (same cell as in A). Currents recorded in 160 TEA-Cl external solution (black) and in the presence of HVA blocker mixture (gray) are shown in themiddle. The resulting subtraction (bottom) shows that most HVA calcium current flows during the shoulder in the action potential. Currents are the average of three sweeps.
