Fig. 1.
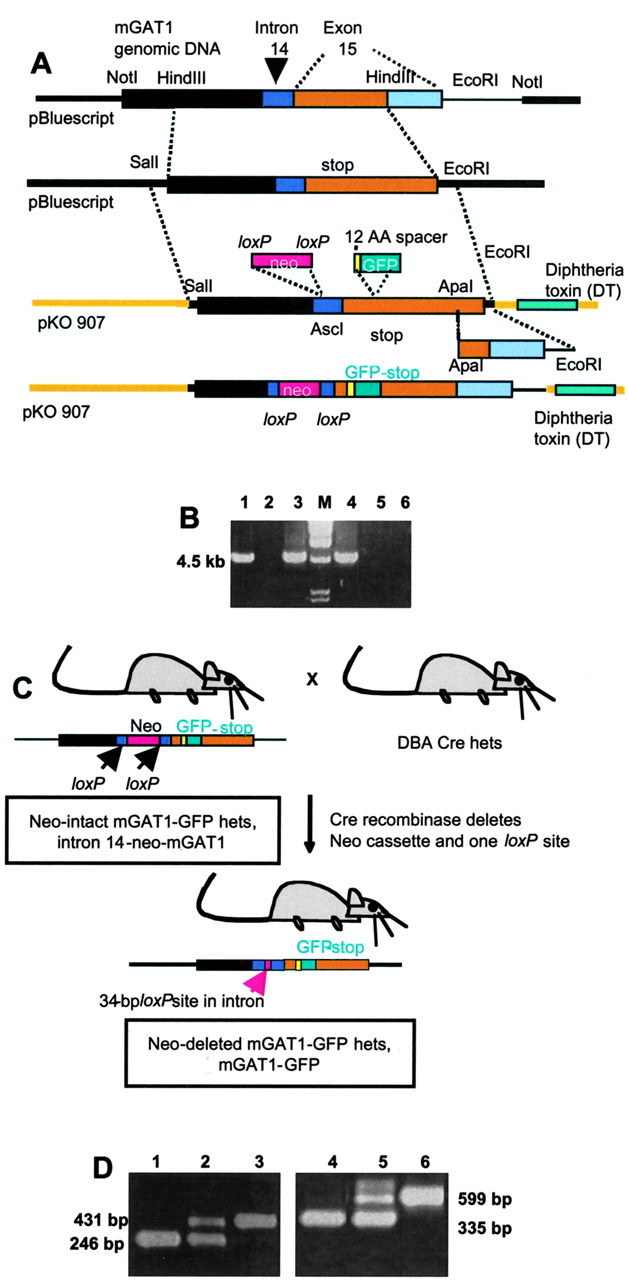
Generation and screening of knock-in strains.A, Modification of mGAT1 genomic DNA to generate a targeting plasmid that contains an mGAT1–GFP fusion sequence in an exon and a floxed neomycin selection cassette in an intron. See Materials and Methods for details. B, PCR screening to identify ES cells carrying the mutant gene. A 4.5 kb PCR product is expected. Lanes 1, 3, and4 represent positive ES cell clones; lane 2 is a negative clone. Lanes 5 and6 show negative controls with no PCR products from genomic DNA extracted from WT ES cells and from the final pKO plasmid construct shown in A. Lane M shows molecular length standards. C, Generation of the Neo-deleted mGAT1–GFP knock-in mouse. The intron 14-Neo-mGAT1 heterozygotes were mated with DBA mice carrying cre recombinase to eliminate the neomycin selection cassette. D, Exemplar PCR genotyping results. Lanes 1–3 show PCR products for mice that are homozygous for the presence of the GFP fusion, heterozygous, and WT, respectively. Lanes 4–6 represent the screening for mice that are homozygous for the presence of the Neo cassette, heterozygous, and WT, respectively.
