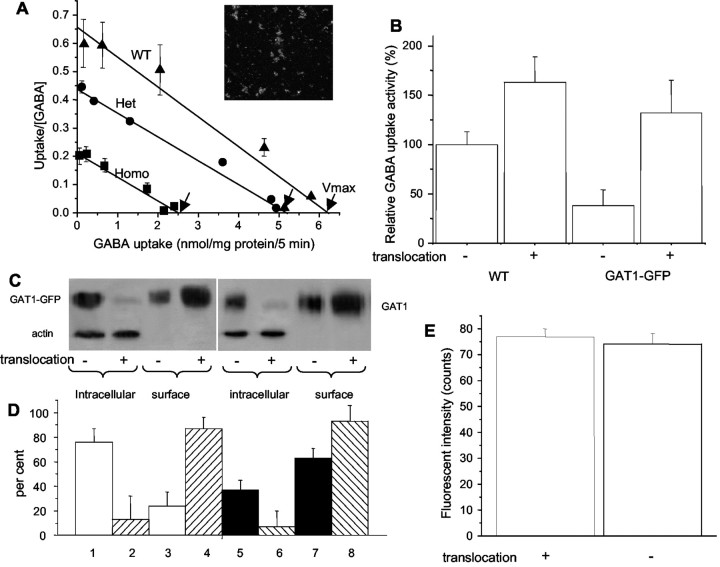
Fig. 7.
GABA uptake and biotinylation assays for mGAT1–GFP partitioning. A, Scatchard plot of [3H]GABA uptake for all three mGAT1–GFP genotypes (mean ± SEM; n = 3). Insetshows image of green fluorescent synaptosomes. B, Manipulation of membrane/cytoplasmic partitioning, assayed by [3H]GABA uptake. Data show NO-711-sensitive [3H]GABA uptake, measured over a time course of 1 hr at 4°C. Synaptosomes were preincubated for 10 min with control solution or subjected to “translocation treatment” with orthovanadate (50 μm), bisindolylmaleimide II (100 nm) to inactivate PKC, and 0.45 m sucrose, all at 4°C. C, Manipulation of membrane/cytoplasmic partitioning, assayed by surface biotinylation of cerebellar slices.Lanes 1–4, Tissue from mGAT1–GFP mice, probed with anti-GFP antibody. Lanes 5–8, Tissue from WT mice, probed with anti-GAT1 antibody. Lanes 1,2, 5, and 6 were also probed with anti-actin antibody. D, Quantitation of immunostaining for mGAT1–GFP and mGAT1 in lanes 1–8.y-axis shows percentage of total staining (intracellular + extracellular) in the pair of lanes denoted by similar patterns.Lane pairs 1 + 3, 2 +4, 5 + 7, and6 + 8 add up to 100%. Data are mean ± SEM from three experiments like that of C.E, Fluorescence intensity in single boutons, untreated or subjected to translocation treatment.