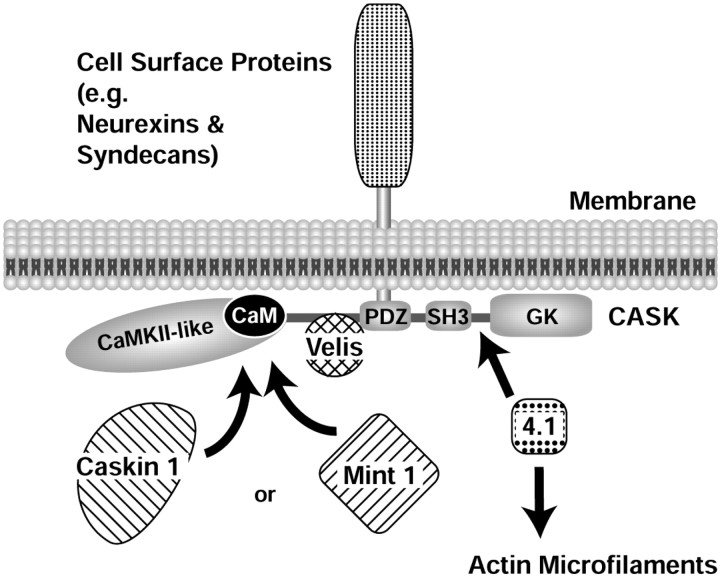
Fig. 13.
Model of the protein–protein interactions mediated by CASK. CASK is recruited to the plasma membrane via interactions of its PDZ domain with the C-terminal cytoplasmic tails of cell-surface proteins, for example neurexins, syndecans, and SynCaM. As a multidomain protein, CASK binds to multiple potential downstream effectors, many of which are also multidomain adaptor proteins containing domains similar to those of CASK. The N-terminal CaM kinase II homology region binds to calmodulin as a function of Ca2+ and to Caskin 1 and Mint 1 independently of Ca2+ (data not shown). The central sequence N-terminal to the PDZ domain binds to Velis, and the C-terminal SH3 and guanylate kinase (GK) domains and connecting sequences bind to protein 4.1, thereby recruiting actin filaments, and to Ca2+ channels (data not shown); in addition, the C-terminal regions may be involved in intramolecular and intermolecular interactions of CASK.