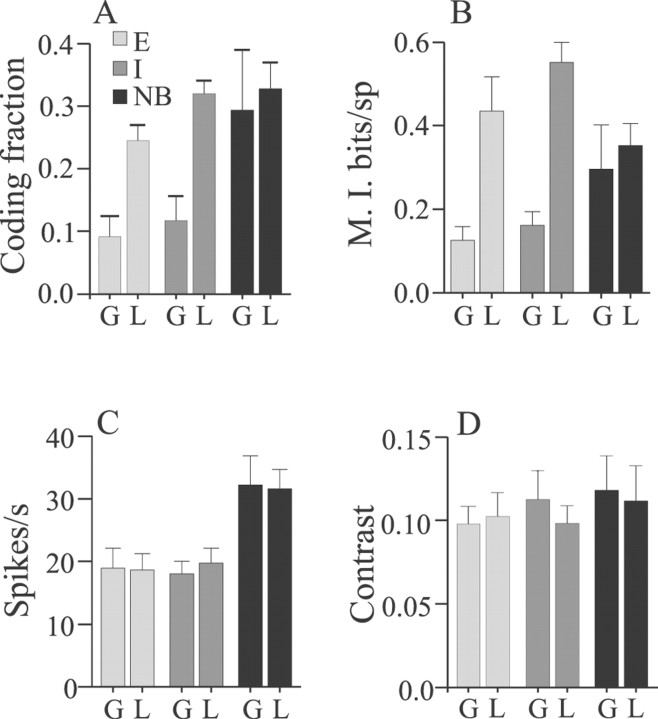
Fig. 11.
Summary of comparisons of coding fraction and mutual information determined from reconstructions of random AM stimuli presented with global (G) or local (L) geometry. A, Mean coding fractions of both E and I cells are significantly greater for stimuli presented with local geometry (p values ≤ 0.001; t tests), but not different for NB cells (p = 0.76). B, Mean mutual information rates of both E and I cells are significantly greater for stimuli presented with local versus global geometry (p values ≤ 0.004; t tests), but not different for NB cells (p = 0.65). Neither mean spike rates during stimulation (C) nor mean stimulus contrasts (D) varied significantly contingent on stimulus geometry for E, I, or NB cells. Error bars = ±1 SEM.