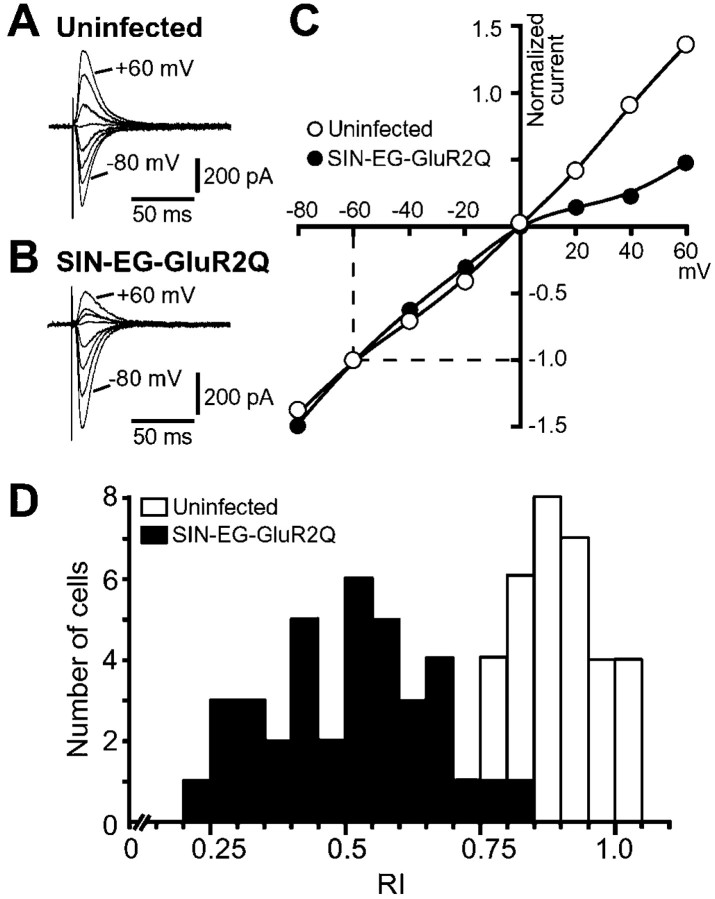
Fig. 4.
Changes in properties of AMPA EPSCs caused by GluR2Q expression at hippocampal MF synapses. A,B, Representative AMPA EPSCs evoked by stimulation of MFs in uninfected (A) and SIN-EG-GluR2Q-infected (B) CA3 pyramidal cells. The EPSCs were recorded at various membrane potentials between −80 and +60 mV in 20 mV steps in the presence of 25 μmd-APV and 20 μm MK-801. To reduce polysynaptic excitation, 5 μm 2-chloroadenosine was also applied to the external solution. C, I–V relationship of AMPA EPSCs shown in A and B. The amplitudes of EPSCs normalized to those at −60 mV were plotted against the holding potential. The open and filled circlesindicate the data from uninfected cells and those infected with SIN-EG-GluR2Q, respectively. D, Histogram showing the distribution of RI values of AMPA EPSCs in SIN-EG-GluR2Q-infected cells (filled bars; n = 37) and uninfected cells (open bars; n = 31).