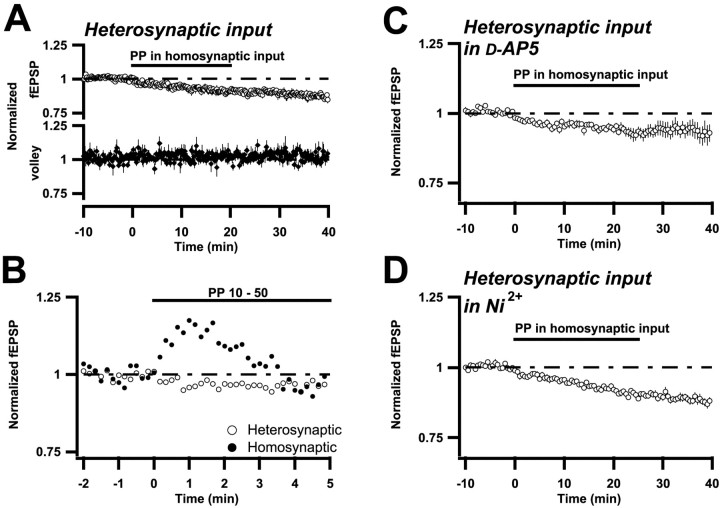
Fig. 4.
PP stimulation induces a synapse specific potentiation, but a synapse nonspecific depression.A–D, Summary plots as described in Results and in Figure 1. The two afferent inputs projecting to the same dendritic region were alternately stimulated at 0.1 Hz. A, Top, Field EPSP changes occurring in one of the inputs (heterosynaptic), when the other input (homosynaptic) was subjected to PP stimulation (n = 8). Bottom, Same but for the presynaptic volley. B, Experiments in which PP stimulation was associated with population spike firing (n = 6). Note that the initial potentiation observed in the homosynaptic input (closed circles) is absent in the heterosynaptic one (open circles).C, Same as in A, but in the presence of 50 μmd-AP-5. Note that each plotted value is the average of three consecutive field EPSPs (n = 7). D, Same as in C, but in the presence of 100 μm Ni2+ (n= 7). Note that the error bars are within the symbols.