Fig. 2.
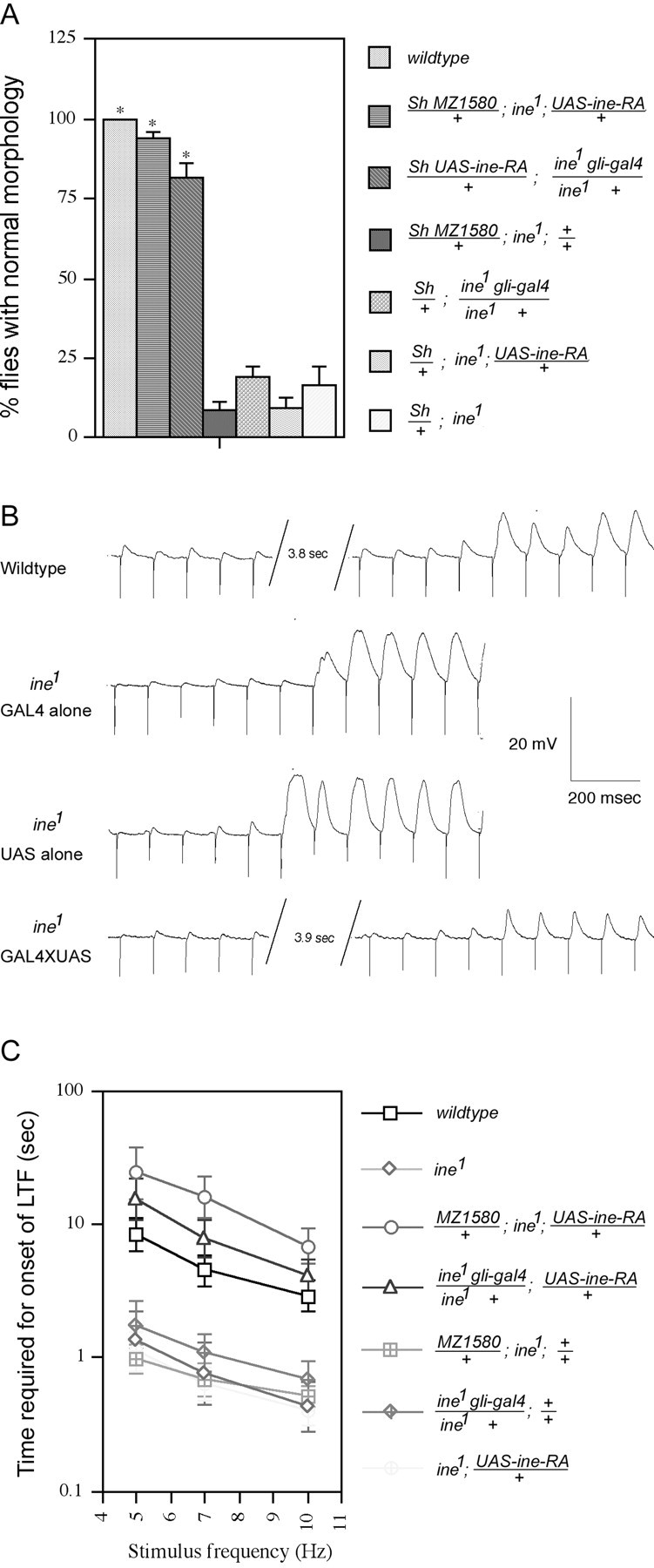
The ine mutant phenotypes are rescued by expression of Ine-P1 in glial cells. Two lines that expressGAL4 in glia, the MZ1580 line and thegli-gal4 line, were used to drive expression of Ine-P1 from the UAS-ine-RA construct. A, Rescue of the downturned wings phenotype. Percentages of flies with normal morphology are shown for each genotype. From top to bottom,n = 200, 97, 82, 130, 131, 104, and 42, respectively, for each genotype. *p < 0.001 versusSh/+; ine1. B,Representative traces showing the increased rate of onset of long-term facilitation in ine1 mutants compared with wild-type larvae, and rescue of this phenotype by reintroduction of Ine-P1 expression in glia. For these traces, GAL4represents MZ1580/+; ine1,UAS representsine1; UAS-ine-RA/+, andGAL4XUAS represents MZ1580/+; ine1‘; UAS-ine-RA/+. C. Quantification of the rescue of the fast long-term facilitation phenotype by expression of Ine-P1 in glia. The bath [Ca2+] was 0.15 mm. A 100 μm concentration of quinidine was present in the recording solution. The time required for the onset of long-term facilitation at the indicated stimulus frequencies is shown for each genotype. From top to bottom,n = 17, 8, 8, 10, 14, 10, and 13, respectively, for each genotype. Error bars represent SEMs.
